Scenic design
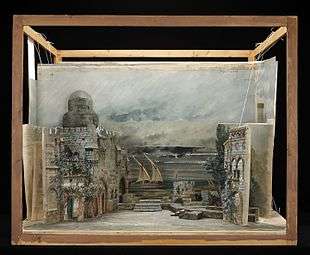
Scenic design (also known as scenography, stage design, set design, or production design) is the creation of theatrical, as well as film or television scenery. Scenic designers come from a variety of artistic backgrounds, but in recent years, are mostly trained professionals, holding a B.F.A. or M.F.A. degrees in theater arts. Scenic designers design sets and scenery that aim to fully immerse the viewer in the production.
Scenic designer
A designer looks at the details searching for evidence through research to produce conceptual ideas that’s best toward supporting the content and values with visual elements. The subject of, “How do we generate creative ideas?” is a very legitimate question. The most consuming part of expanding our horizons toward scenic concepts is much more than witnessing creativity, and creative people. It starts with us opening our mind to the possibilities. To have an attitude toward learning, seeking, and engaging in creativity and to be willing to be adventurous, inquisitive and curious. Our imagination is highly visual. Whether outside or inside, colorful trees or concerts, star lit skies or the architecture of a great building, scenic design is a process of discovery. Discovering what will best clarify and support the story being told.
The scenic designer works with the director and other designers to establish an overall visual concept for the production and design the stage environment. They are responsible for developing a complete set of design drawings that include the following:
- basic ground plan showing all stationary scenic elements;
- composite ground plan showing all moving scenic elements, indicating both their onstage and storage positions;
- section of the stage space incorporating all elements;
- front elevations of every scenic element, and additional elevations or sections of units as required.
All of these required drawing elements can be easily created from one accurate 3-D CAD model of the set design.
Responsibility

The scenic designer is responsible for collaborating with the theatre director and other members of the production design team to create an environment for the production and then communicating the details of this environment to the technical director, production manager, charge scenic artist and prop master. Scenic designers are responsible for creating scale models of the scenery, renderings, paint elevations and scale construction drawings as part of their communication with other production staff.
Training
In Europe and Australia,[1] scenic designers take a more holistic approach to theatrical design and will often be responsible not only for scenic design but costume, lighting and sound and are referred to as theatre designers or scenographers or production designers.
Notable scenic designers, past and present, include: Adolphe Appia, Boris Aronson, Alexandre Benois, Alison Chitty, Antony McDonald, Barry Kay, Caspar Neher, Cyro Del Nero, Aleksandra Ekster, Daniil Lider, David Borovsky, David Gallo, Edward Gordon Craig, Es Devlin, Ezio Frigerio, Franco Colavecchia, Christopher Gibbs, Franco Zeffirelli, George Tsypin, Howard Bay, Inigo Jones, Jean-Pierre Ponnelle, Jo Mielziner, John Lee Beatty, Josef Svoboda, Ken Adam, Léon Bakst, Luciano Damiani, Maria Björnson, Ming Cho Lee, Motley, Natalia Goncharova, Nathan Altman, Nicholas Georgiadis, Oliver Smith, Ralph Koltai, Neil Patel, Robert Brill, Robert Wilson, Russell Patterson, Brian Sidney Bembridge, Santo Loquasto, Sean Kenny, Todd Rosenthal, Robin Wagner, Tony Walton.
See also
References
- ↑ "Training as a Theatre Designer". Central School of Speech and Drama, University of London article.
Further reading
- Making the Scene: A History of Stage Design and Technology in Europe and the United States by Oscar G. Brockett, Margaret Mitchell, and Linda Hardberger (Tobin Theatre Arts Fund, distributed by University of Texas Press; 2010) 365 pages; traces the history of scene design since the ancient Greeks.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Scenography. |
- Prague Quadrennial of Performance Design and Space - the largest scenography event in the world - presenting contemporary work in a variety of performance design disciplines and genres - costume, stage, light, sound design, and theatre architecture for dance, opera, drama, site specific, multi-media performances, and performance art, etc., Prague, CZ
- What is Scenography Article illustrating the differences between US and European theatre design practices
Special:WhatLinksHere/Julia Anastasopoulos