Sterkfontein Dam
| Sterkfontein Dam | |
|---|---|
 Sterkfontein Dam Reservoir seen from the R74 | |
 Location of Sterkfontein Dam in South Africa | |
| Official name | Sterkfontein Dam |
| Location | Free State |
| Coordinates | 28°26′54″S 29°01′22″E / 28.4484°S 29.0228°ECoordinates: 28°26′54″S 29°01′22″E / 28.4484°S 29.0228°E |
| Construction began | 1969 |
| Opening date | 1980 (renovated 1986)[1] |
| Dam and spillways | |
| Type of dam | Earth fill dam |
| Impounds | Nuwejaarspruit[1] |
| Height | 97 metres (320 ft)[1] |
| Length | 3,060 metres (3,350 yd)[1] |
| Dam volume | 19,800,000 m3 (25,900,000 cu yd) |
| Spillway capacity | 0 m3/s (0 cu ft/s) |
| Reservoir | |
| Creates | Sterkfontein Dam Reservoir |
| Total capacity | 2,616,000 ML (2,121,000 acre·ft)[1] |
| Catchment area | 195 km2 (75 sq mi) |
| Surface area | 69.37 km2 (26.78 sq mi)[1] |
| Max. length | 18.8 km (11.7 mi) |
| Normal elevation | 1,708 m (5,604 ft) |
The Sterkfontein Dam, located just outside the town of Harrismith, in the Free State, province of South Africa, is part of the Tugela-Vaal Water Project and the Drakensberg Pumped Storage Scheme, and located on the Nuwejaarspruit, a tributary of the Wilge River in the upper catchment area of the Vaal River.[2]
Background
History
The rapid economic expansion of the greater Johannesburg area in the 1960s and 70s put its water supply under long term threat and it was decided to redirect water from the large Tugela River which was going largely un-used into the sea and store it in large strategic water storage reservoir with very low evaporation. The initial site chosen for this project was in the adjacent valley to the west on the Elands River. This was the preferred option from an engineering aspect because it would involve a smaller dam wall. However shortly before construction was about to start the site on the Nuwejaarspruit was selected for political reasons because it avoided the partial flooding the newly planned Apartheid era Bantustan of Qwaqwa in Phuthadichaba. Under the peculiar politics of the time it potentially could have meant this strategic national resource could have been located in a "foreign country" which would have been unacceptable as seen from the perspective of Apartheid Government.
Construction
Construction began in 1969 and the first phase was commissioned in 1977 and comprised a 69-metre (226 ft) high earthfill embankment 2,290 metres (7,510 ft) long with no spillway. After completion of the first phase the decision was made to immediately continue with the final phase and it was subsequently raised in 1980 to its current height of 93 metres (305 ft) with a crest length of 3,060 metres (10,040 ft) and a full supply capacity of 2,656 million cubic metres (2,153,000 acre·ft). At full supply, it has a surface area of no more than 70 km2. The extended dam was commissioned in 1980, and has a capacity of 2,616,950 cubic metres (2,121.60 acre·ft), with a surface area of only 67.26 square kilometres (25.97 sq mi), the dam wall is 93 metres (305 ft) high. The total construction period was 11 years. The Sterkfontein Dam was designed and constructed by the Department of Water Affairs. The dam mainly serves for domestic and industrial use and its hazard potential has been ranked high (3).
Naming
The dam was named after one of the many farms expropriated in its construction. The temporary township for the construction workers was built on the Sterkfontein farm. The word sterkfontein means "strong fountain" when translated from Afrikaans.
Characteristics
Earth Fill Dam Wall
The wall is an earth gravity type. The dam wall contains 19.8 million cubic metres (700×106 cu ft) of material making it the largest dam wall in South Africa with regard to volume. The reservoir is impounded by two walls. The second wall is 600 metres (2,000 ft) long and contains 1.04 million cubic metres (37×106 cu ft) of material.
No spillway
This dam is rather unique in that very little of its water is sourced is from rainfall. The dam was not built on a river but instead it is sited on what can at best be classed as a large stream in the upper reaches of a valley on the Nuwejaarspruit. The catchment area of the dam is less than three times the water surface area of the dam and therefore not risk to a flood. For this reason the main dam wall does not have the need for a spillway. Any excess rain water can be safely ejected from its oulet valves. The advantage of this location is the Dam is a highly effective reservoir, since it has the depth to store a large amount of water, with very little loss to evaporation. The Vaal Dam lake (reservoir) by comparison has a large surface area and is relatively shallow, which results in a higher rate of evaporation. It would take 17 years of rainfall to fill the dam. But capturing rainfall was not an important intent behind this project. It was built to capture water from the Tugela river and deliver it into the Vaal system.
Pumped Hydro Storage Scheme
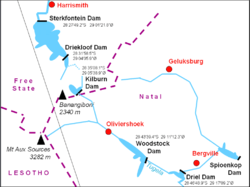
The dam receives its water via the Tugela-Vaal Water Project later renamed the Drakensberg Pumped Storage Scheme which is a 1,000 MW pumped hydro storage scheme involving the net transfer of up to 630 million cubic metres (510,000 acre·ft) of water from KwaZulu-Natal. This is stored in the Sterkfontein Dam and released to the Vaal Dam via the Wilge River when needed.
A dam within a dam

The Driekloof Dam which is inside the Sterkfontein Dam, is regarded as a separated dam and reservoir, and is not included in the above figures. It is essentially a dam within a dam. Driekloof Dam is the upper storage reservoir of the Drakensberg Pumped Storage Scheme. If the Sterkfontein Dam were to be empty the Driekloof reservoir would retain the water for the pumped storage scheme to operate unimpeded. When Sterkfontein Dam is at full capacity the Driekloof Dam is submerged up to the top of its spillway.
Third largest dam in South Africa
This is the 3rd largest dam in South Africa in terms of water capacity and it is slightly larger than Vaal Dam.
- Gariep Dam 5,340,600 MegaL
- Vanderkloof Dam 3,171,300 MegaL
- Sterkfontein Dam 2,616,900 MegaL
- Vaal Dam 2,603,400 MegaL
Protected areas
The Sterkfontein Dam Nature Reserve is a protected area located by the dam.[3]
Photo gallery
 Artists impression of the 1st phase of the Sterkfontein Dam. The final wall was raised to the level of the valve control room at the top of the concrete tower.
Artists impression of the 1st phase of the Sterkfontein Dam. The final wall was raised to the level of the valve control room at the top of the concrete tower. A view of the dam basin prior to being covered by water.
A view of the dam basin prior to being covered by water.- The first of three information boards posted at a vehicle rest area overlooking the reservoir just off the R74.
- The second information board.
- The third information board.
- A campsite with chalets at the water's edge. Note the dry conditions (conducive to bush fires) in the wintertime.
- Camping area at the water's edge.
 The earth wall on the eastern side of the Sterkfontein Dam.
The earth wall on the eastern side of the Sterkfontein Dam. Earth moving equipment dumping fill from the borrow pits for the wall of Sterkfontein Dam. Aug 1972
Earth moving equipment dumping fill from the borrow pits for the wall of Sterkfontein Dam. Aug 1972 The site workshops for Sterkfontein Dam. The area below the site office is now underwater.
The site workshops for Sterkfontein Dam. The area below the site office is now underwater. The construction village at Sterkfontein Dam 1973
The construction village at Sterkfontein Dam 1973 The Department of Water Affairs site office. Sterkfontein Dam 1972
The Department of Water Affairs site office. Sterkfontein Dam 1972 A view of the dam wall of Sterkfontein Dam during construction. In the foreground is resident Engineer David Bell.
A view of the dam wall of Sterkfontein Dam during construction. In the foreground is resident Engineer David Bell. David Bell the Resident Engineer of Sterkfontein Dam explaining the works to a journalist. Circa 1974
David Bell the Resident Engineer of Sterkfontein Dam explaining the works to a journalist. Circa 1974
See also
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "STERKFONTEIN DAM". Department of Water Affairs and Forestry. Retrieved 2008-10-22.
- ↑ Upper Vaal WMA 8
- ↑ Free State Tourism - Sterkfontein Dam Nature Reserve
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Sterkfontein Dam. |
|
|