Tympanic nerve
| Tympanic nerve | |
|---|---|
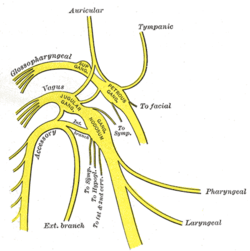 Plan of upper portions of glossopharyngeal, vagus, and accessory nerves. (Tympanic nerve visible in upper right) | |
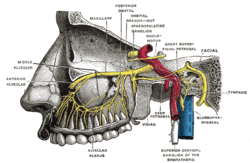 Tympanic nerve (labelled right side) | |
| Details | |
| To | tympanic plexus |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | nervus tympanicus |
| TA | A14.2.01.138 |
| FMA | 53480 |
The tympanic nerve (nerve of Jacobson) is a branch of the glossopharyngeal nerve found near the ear.
Path
It arises from the petrous ganglion, and ascends to the tympanic cavity through a small canal, the inferior tympanic canaliculus, on the under surface of the petrous portion of the temporal bone on the ridge which separates the carotid canal from the jugular fossa.
In the tympanic cavity it divides into branches which form the tympanic plexus and are contained in grooves upon the surface of the promontory.
Jacobson's nerve contains both sensory and secretory fibers.
- Sensory fibers supply the middle ear.
- Parasympathetic secretory fibers continue as the Lesser Petrosal nerve and provide secretomotor innervation to the parotid gland. The secretory fibers enter the otic ganglion.
- Sympathetic fibers (for the large deep petrosal nerve) through communication with the carotid plexus
The postganglionic parasympathetic fibers are then distributed via the auriculotemporal nerve (branch of the trigeminal nerve) to the parotid gland.
Clinical significance
This nerve may be involved by paraganglioma, in this location referred to as glomus jugulare or glomus tympanicum tumours.
Additional images
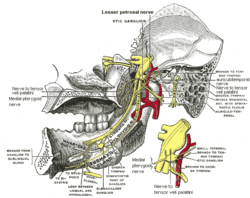 Lesser petrosal nerve
Lesser petrosal nerve
References
This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
- Tympanic and Lesser petrosal nerve diagram
- cranialnerves at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (IX)