Underwater photography

_with_Elacatinus_oceanops_(Neon_Goby).jpg)

Underwater photography is the process of taking photographs while under water. It is usually done while scuba diving, but can be done while diving on surface supply, snorkeling, swimming, from a submersible or remotely operated underwater vehicle, or from automated cameras lowered from the surface.
Underwater photography can also be categorised as an art form and a method for recording data.
Successful underwater imaging is usually done with specialized equipment and techniques. However, it offers exciting and rare photographic opportunities. Animals such as fish and marine mammals are common subjects, but photographers also pursue shipwrecks, submerged cave systems, underwater "landscapes", invertebrates, seaweeds, geological features, and portraits of fellow divers.
Lighting
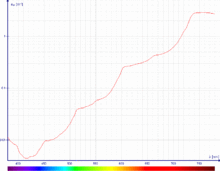
The primary obstacle faced by underwater photographers is the loss of color and contrast when submerged to any significant depth. The longer wavelengths of sunlight (such as red or orange) are absorbed quickly by the surrounding water, so even to the naked eye everything appears blue-green. The loss of color increases not only vertically through the water column, but also horizontally, so subjects farther away from the camera also appear colorless and indistinct. This effect occurs in apparently clear water, such as that found around tropical coral reefs.[1]
Underwater photographers solve this problem by combining two techniques. The first is to get the camera as close to the photographic subject as possible, minimizing the horizontal loss of color. Many serious underwater photographers consider any more than about one yard or meter unacceptable. The second technique is the use of a flash to restore colour lost to depth. Fill flash, used effectively, "paints" in missing colors by providing full-spectrum visible light to the overall exposure.[2]
Another environmental effect is range of visibility. The water is seldom optimally clear, and the dissolved and suspended matter can reduce visibility by both absorption and scattering of light.
Equipment
Some cameras are made for use underwater, including modern waterproof digital cameras. The first amphibious camera was the Calypso, reintroduced as the Nikonos in 1963. The Nikonos range was designed specifically for use underwater. Nikon ended the Nikonos series in 2001[3] and its use has declined, as has that of other 35mm film systems. Sea and Sea USA made the Motor Marine III, an amphibious range-finder camera for 35mm film.[4][5]



Cameras made for dry work can also work underwater, protected by add-on housings, which are made for point and shoot cameras, compact cameras with full exposure controls, and single lens reflex cameras (SLRs). Most such housings are specific to the camera. Materials range from relatively inexpensive plastic to high-priced aluminum. Housings allow many options: users can choose housings specific to their everyday "land" cameras and use any lens. Underwater photographers generally use wide-angle lenses or macro lenses, both of which allow close focus and therefore a shorter distance to the subject, which reduces the loss of clarity to scattering. Digital media can hold many more shots than standard film (which rarely has more than 36 frames per roll). This gives digital cameras an advantage, since it is impractical to change film underwater. Other comparisons between digital and film photography also apply, and the use of film under water has declined, as it has on land.
Underwater housings have control knobs and buttons that reach the camera inside, allowing use of most of its normal functions. These housings may also have connectors to attach external flash units. Some basic housings allow the use of the flash on the camera, but the on-board flash may not be powerful enough or properly placed for underwater use. More-advanced housings either redirect the on-board strobe to fire a slave strobe via a fiber-optic cable, or physically prevent the use of the on-board strobe. Housings are made waterproof by silicone or other elastomer O-rings at the crucial joints and where control spindles and pushbuttons pass through the housing. High-end housings may use double O-rings on many of the critical pushbuttons and spindles to reduce the risk of leaks, which can destroy the electronics in cameras. Some cameras are inherently waterproof, or submersible to shallow depths; when these are in submersible housings, the consequences of a small leak are generally not serious.
There are optical problems with using cameras inside a watertight housing. Because of refraction, the image coming through the glass port will be distorted, especially with wide-angle lenses. A dome-shaped or fish-eye port corrects this distortion. Most manufacturers make these dome ports for their housings, often designing them to be used with specific lenses to maximize their effectiveness. The Nikonos series allowed the use of water-contact optics—lenses designed to be used submerged, without the ability to focus correctly when used in air. There is also a problem with some digital cameras, which do not have sufficiently wide lenses built in; to solve this, there are housings made with supplementary optics in addition to the dome port, making the apparent angle of view wider. Some housings work with wet-coupled lenses, which are screwed on to the outside of the lens port and increase the field of view; these lenses may be added or removed under water, allowing both macro and wide-angle photography on the same dive.
With macro lenses, the distortion caused by refraction is not a problem, so normally a simple flat glass port is used. Refraction increases the magnification of a macro lens; this is considered a benefit to photographers who are trying to capture very small subjects.
Underwater flash

The use of a flash or strobe is often regarded as the most difficult aspect of underwater photography. Some misconceptions exist about the proper use of flash underwater, especially as it relates to wide-angle photography. Generally, the flash should be used to supplement the overall exposure and to restore lost color, not as the primary light source. In situations such as the interior of caves or shipwrecks, wide-angle images can be 100% strobe light, but such situations are fairly rare. Usually, the photographer tries to create an aesthetic balance between the available sunlight and the strobe. Deep, dark or low visibility environments can make this balance more difficult, but the concept remains the same. Many modern cameras have simplified this process through various automatic exposure modes and the use of through-the-lens (TTL) metering. The increasing use of digital cameras has reduced the learning curve of underwater flash significantly, since the user can instantly review photos and make adjustments.
Color is absorbed as it travels through water, so that the deeper you are, the less reds, oranges and yellow colors remain. The strobe replaces that color. It also helps to provide shadow and texture, and is a valuable tool for creativity.
An added complication is the phenomenon of backscatter, where the flash reflects off particles or plankton in the water. Even seemingly clear water contains enormous amounts of this particulate, even if it is not readily seen by the naked eye. The best technique for avoiding backscatter is positioning the strobe away from the axis of the camera lens. Ideally, this means the flash will not light up the water directly in front of the lens, but will still strike the subject. Various systems of jointed arms and attachments are used to make off-camera strobes easier to manipulate.

When using macro lenses, photographers are much more likely to use 100% strobe light for the exposure. The subject is normally very close to the lens, and the available sunlight is usually not sufficient.
There have been some attempts to avoid the use of flash entirely, but these have mostly failed. In shallow water, the use of custom white-balance provides excellent color without the use of strobe. In theory one could use color filters to overcome the blue-green shift, but this can be problematic. The amount of shift would vary with depth and turbidity, and there would still be a significant loss of contrast. Many digital cameras have settings that will provide color balance, but this can cause other problems. For example, an image shifted toward the "warm" part of the spectrum can create background water which appears gray, purple or pink, and looks unnatural. There have been some successful experiments using filters combined with the raw image format function on some high-end digital cameras, allowing more detailed manipulation in the digital darkroom. This approach will probably always be restricted to shallower depths, where the loss of color is less extreme. In spite of that, it can be effective for large subjects such as shipwrecks which could not be lit effectively with strobes.

Natural light photography underwater[6] can be beautiful when done properly with subjects such as upward silhouettes, light beams, and large subjects such as whales and dolphins.
Although digital cameras have revolutionized many aspects of underwater imaging, it is unlikely that flash will ever be eliminated completely. From an aesthetic standpoint, the flash emphasizes the subject and helps separate it from the blue background, especially in deeper water. Ultimately the loss of color and contrast is a pervasive optical problem that cannot always be adjusted in software such as Photoshop.
Split images

Another format considered part of underwater photography is the over/under or split image, a composition that includes roughly half above the surface and half underwater. The traditional technique was pioneered by National Geographic photographer David Doubilet, who used it to capture scenes above and below the surface simultaneously. Split images are popular in recreational scuba magazines, often showing divers swimming beneath a boat, or shallow coral reefs with the shoreline seen in the background.
Over/under shots present some technical challenges beyond the scope of most underwater camera systems. Normally a wide-angle lens is used, similar to the way they are used in everyday underwater photography. However, the exposure value in the "air" part of the image is often quite different from the one underwater. There is also the problem of refraction in the underwater segment, and how it affects the overall focus in relation to the air segment. There are specialized split filters designed to compensate for both of these problems, as well as techniques for creating even exposure across the entire image. Some photographers also use extremely wide or fisheye lenses, which have enough depth of field to overcome any differences in focus. One must also take into account the "dome" of the underwater camera housing. A wider dome is better for over/under shots as it lets the water rest. Some photographers use an external flash underwater on a low setting to overcome the difference in usable light in the two areas.
Digital darkroom techniques can also be used to "splice" two images together, creating the appearance of an over/under shot.
Skills and training
Since underwater photography is often performed while scuba diving, it is important that the diver-photographer be sufficiently skilled so that it remains a reasonably safe activity. Good scuba technique also improves the quality of images, since marine life is less likely to be scared away by a calm diver, and the environment is less likely to be damaged or disturbed. There is the possibility of encountering poor conditions, such as heavy currents, tidal flow, or poor visibility. Underwater photographers usually try to avoid these situations whenever possible. Underwater diving training providers provides courses to help improve divers' diving skills and underwater photography skills.[7]
Timeline


- 1856 — William Thompson takes the first underwater pictures using a camera mounted on a pole.
- 1893 — Louis Boutan takes underwater pictures in Banyuls-sur-Mer while diving using a surface supplied hard hat diving gear. He also develops an underwater flash and a remote control for deep waters using an electromagnet.[8]
- 1914 — John Ernest Williamson shoots the first underwater motion picture in the Bahamas.[9]
- 1926 — William Harding Longley and Charles Martin take the first underwater colour photos using a magnesium-powered flash.
- 1940- — Bruce Mozert begins to photograph at Silver Springs, Florida
- 1957 — The CALYPSO-PHOT camera is designed by Jean de Wouters and promoted by Jacques-Yves Cousteau. It is first released in Australia in 1963. It features a maximum 1/1000 second shutter speed. A similar version is later produced by Nikon as the Nikonos, with a maximum 1/500 second shutter speed and becomes the best-selling underwater camera series.
- 1961 — The San Diego Underwater Photographic Society is established, one of the earliest organizations dedicated to the advancement of underwater photography.
See also
- Diving equipment
- List of basic photography topics
- Nature photography
- Underwater photography (sport)
- Underwater photography world championships
- Underwater videography
- Waterproof digital camera
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Underwater photography. |
- ↑ Deep-six.com Color underwater
- ↑ Scott Gietler Underwater Photography Guide Lighting with Strobes
- ↑ 'NIKONOS-V camera body to be discontinued', September 18, 2001, , retrieved 03/09/2012.
- ↑ "Sea and Sea". Sea and Sea. Retrieved 2012-06-20.
- ↑ Staff. "Motor Marine III Instruction Manual" (PDF). Sea and Sea. Retrieved 7 November 2016.
- ↑ "Natural Light Photography". Retrieved December 25, 2013.
- ↑ PADI Course Flowchart
- ↑ Cárdenas, Fabricio (2014). 66 petites histoires du Pays Catalan [66 Little Stories of Catalan Country] (in French). Perpignan: Ultima Necat. ISBN 978-2-36771-006-8. OCLC 893847466.
- ↑ "Thirty leagues under the sea". The Independent. Nov 2, 1914. Retrieved July 24, 2012.

