Volley fire

Volley fire, as a military tactic, is in its simplest form the concept of having soldiers shoot in turns.[1] In practice, it often consists of having a line of soldiers all fire their weapons simultaneously at the enemy forces on command. This is usually to make up for the inaccuracy, slow rate of fire, and limited range of a weapon which requires extensive effort to reload. The volley fire, specifically the musketry volley technique, also known as the countermarch, requires lines of soldiers to fire on command and march back into a column to reload while the next row shoots, and so repeat fire. While this tactic is usually associated with Dutch military thinkers in the late 16th century, its principles have been applied to crossbow infantry since at least the Tang dynasty.[2]
History
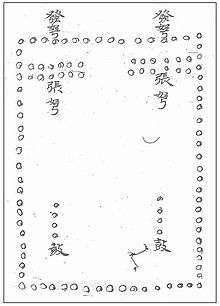
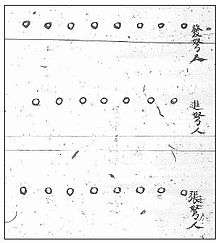





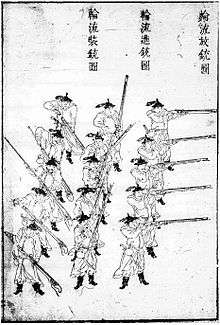

Although volley fire is most often associated with firearms, the concept of continuous and concerted rotating fire was practiced using crossbows since at least the Tang dynasty.[2] The 759 CE text Tai bai yin jing (太白陰經) by Tang military official Li Quan (李筌) contains the oldest known extant depiction and description of the volley fire technique. The Tang crossbow volley fire formation was rectangular and the illustration shows each circle as one soldier. In the front is a line labeled "shooting crossbows" (發弩) and behind that line are shorter rows of crossbowmen, two facing right and two facing left, and they are labeled "loading crossbows" (張弩). The commander (大將軍) is situated in the middle of the formation and to his right and left are vertical rows of drummers (鼓) who coordinate the firing and reloading procedure in procession: who loaded their weapons, stepped forward to the outer ranks, shot, and then retired to reload.[3] According to Li Quan, "the classics say that the crossbow is fury. It is said that its noise is so powerful that it sounds like fury, and that's why they named it this way,"[4] and by using the volley fire method there is no end to the sound and fury, and the enemy is unable to approach.[4] Here he is referring to the word for "crossbow" nu which is also a homophone for the word for fury nu.[2]
The famous encyclopedic text known as the Tongdian by Du You from 801 CE also provides a description of the volley fire technique: "[Crossbow units] should be divided into teams that can concentrate their arrow shooting.… Those in the center of the formations should load [their bows] while those on the outside of the formations should shoot. They take turns, revolving and returning, so that once they've loaded they exit [i.e., proceed to the outer ranks] and once they've shot they enter [i.e., go within the formations]. In this way, the sound of the crossbow will not cease and the enemy will not harm us."[2]
While the virtues of volley fire was understood during the Tang dynasty, the Wujing Zongyao written during the Song dynasty notes that it was not utilized to its full effectiveness due to their fear of cavalry charges.[3] The author's solution was to drill the soldiers to the point where rather than hide behind shield units upon the approach of melee infantry, they would "plant the feet like a firm mountain, and, unmoving at the front of the battle arrays, shoot thickly to the middle [of the enemy], and none among them will not fall down dead."[3] The Song volley fire formation was described thus: "Those in the center of the formation should load while those on the outside of the formation should shoot, and when [the enemy gets] close, then they should shelter themselves with small shields [literally side shields, 旁牌], each taking turns and returning, so that those who are loading are within the formation. In this way the crossbows will not cease sounding."[3] In addition to the Tang formation, the Song illustration also added a new label to the middle line of crossbowmen between the firing and reloading lines, known as the "advancing crossbows."[5] Both Tang and Song manuals also made aware to the reader that "the accumulated arrows should be shot in a stream, which means that in front of them there must be no standing troops, and across [from them] no horizontal formations."[5]
The volley fire technique was used to great effect by the Song during the Jin-Song Wars. In the fall of 1131 the Jin commander Wuzhu (兀朮) invaded the Shaanxi region but was defeated by general Wu Jie (吳 玠) and his younger brother Wu Lin (吳璘). The History of Song elaborates on the battle in detail:
[Wu] Jie ordered his commanders to select their most vigorous bowmen and strongest crossbowmen and to divide them up for alternate shooting by turns (分番迭射). They were called the "Standing-Firm Arrow Teams" (駐隊矢), and they shot continuously without cease, as thick as rain pouring down. The enemy fell back a bit, and then [Wu Jie] attacked with cavalry from the side to cut off the [enemy's] supply routes. [The enemy] crossed the encirclement and retreated, but [Wu Jie] set up ambushes at Shenben and waited. When the Jin troops arrived, [Wu's] ambushers shot, and the many [enemy] were in chaos. The troops were released to attack at night and greatly defeated them. Wuzhu was struck by a flowing arrow and barely escaped with his life.[6]— History of Song Tonio Andrade translation
After his defeat and losing half his army Wuzhu escaped back to the north, only invade again in the following year. Again, he was defeated while trying to breach a strategic pass. The History of Song states that during the battle Wu Jie's brother Wu Lin "used the Standing-Firm Arrow Teams, who shot alternately, and the arrows fell like rain, and the dead piled up in layers, but the enemy climbed over them and kept climbing up."[7] This passage is especially noteworthy for its mention of a special technique being utilized as it is one of the very few times that the History of Song has elaborated on a specific tactic.[7]
The crossbow volley fire remained a popular tactic into the Ming dynasty. The martial artist Cheng Chongdou, who studied at the Shaolin Temple, was a particularly avid proponent of the mixed crossbow volley and melee infantry force, which would ideally carry both a wearable crossbow strapped behind the back as well as a personal melee weapon such as the lance or sword. He provides a detailed description of the volley fire technique in a military text ca. 1621:
The ancients used ten thousand crossbows shooting in concert to win victories over enemies, and today I will describe it succinctly. Suppose you have three hundred crossbowmen. The first hundred of them have already loaded their arrows and are already arrayed together in the front. They are labeled "shooting crossbows." The next hundred crossbowmen have also already loaded their arrows, but they are arrayed together in the next row and are labeled "advancing crossbows." Finally, the last hundred men are arrayed behind them, in [the third and] last row. They are loading their crossbows and are labeled "loading crossbows." The first hundred men, which is to say the "shooting crossbows," shoot. After they are done they retire to the rear, at which the second hundred men, the "advancing crossbows," move to the fore and themselves become "shooting crossbows." The rear hundred men, which is to say the "loading crossbows," move forward and become the "advancing crossbows." When the first hundred men have fired and returned to the back, they become "loading crossbows." And in this way they revolve and take turns firing a constant stream, and the crossbows sound without cease.[8]— Jue zhang xin fa, chang qiang fa xuan, dan dao fa xuan Tonio Andrade translation
In Europe volley fire was also used by archers, for example at the Battle of Agincourt in 1415.[9]
The earliest possible occurrence of volley fire for firearms first appeared in late 14th century China during a conflict between the Ming and Mong Mao forces. Volley fire was also possibly implemented with firearms in 1414 during the Yongle Emperor's campaigns against the Mongols, and possibly again in another expedition in 1422. However the language used in these sources is unclear as to whether or not repeating fire was part of the technique implemented by the Ming. For example during the 1388 anti-insurrection war waged against the Mong Mao by the Ming general Mu Ying, the Ming troops equipped with guns and fire arrows were arrayed in three lines. The general Mu Ying explained this was so that "when the elephants advance, the front line of guns and arrows will shoot all at once. If they do not retreat, the next line will continue this. If they still do not retreat, then the third line will continue this."[10] When the armored war elephants broke into a run, charging the Ming lines, the Ming forces stood their ground, "shooting arrows and stones, the noise shaking the mountains and vallies. The elephants shook with fear and ran."[10] According to the Ming Shilu, half the elephants were killed while 37 were captured, and of the 100,000 strong insurrection force, at least 30,000 were killed, and 10,000 were captured.[11] Andrade and other historians have interpreted this passage as evidence of volley fire, however he admits that it is ambiguous as to whether or not the Ming lines practiced repeated fire and reloading, so at best it can only be considered a limited form of volley fire.[11]
The Ming Shilu goes on to mention another possible instance of volley fire, this time during the Yongle Emperor's campaigns against the Mongols. In 1414 "the commander-in-chief (都督) Zhu Chong led Lü Guang and others directly to the fore, where they assaulted the enemy by firing firearms and guns continuously and in succession. Countless enemies were killed."[11] In this case the source makes no mention of taking turns or forming lines, but Andrade believes that since the Ming were facing horseback Mongol forces, it would have been impossible to keep continuous fire in the face of a cavalry charge had volley fire not been implemented.[11] The same rationality is applied to another passage on the 1422 expedition, where "the emperor ordered that all the generals train their troops outside each encampment by arranging their formations so that the gunnery units (神機銃) occupied the foremost positions and the cavalry units occupied the rear. He ordered officers to exercise and drill in their free time (暇閑操習). He admonished them as follows: "A formation that is dense is solid, while an advance force is sparse, and when they arrive at the gates of war and it's time to fight, then first use the guns to destroy their advance guard and then use cavalry to rush their solidity. In this way there is nothing to fear.""[12] Some historians have extrapolated from this that the Ming forces were using volley fire with firearms since their opponents were cavalry units, and hence impossible to stop with slow firing hand cannons unless it was through continuous volley fire, much less with a thin advance guard of gunnery units. According to Wang Zhaochun, "the meaning of this is that when fighting, the gun troops line up in front of the entire formation, and between them there must be a certain amount of space, so that they can load bullets and powder and employ shooting by turns and in concert to destroy the enemy advance guard. Once the enemy has been thrown into chaos, the rear densely arrayed cavalry troops together come forth in great vigor, striking forth with irresistible force."[13] Even if Wang is correct, the evidence is still inconclusive.[13]
The volley tactic next appeared in early 16th century Europe when the Ottoman Janissaries clashed with European forces at the Battle of Mohács on 29 August 1526.[2] The Janissaries equipped with 2000 tüfenks (usually translated as musket) "formed nine consecutive rows and they fired their weapons row by row,"[14] in a "kneeling or standing position without the need for additional support or rest."[14] Contrary to the popular belief that the Ottomans' success at Mohács was due to their artillery, a view which many later historians have supported, European and Ottoman sources on the battle attribute their success to the Janissaries' successful deployment of firearms.[14] However the Janissaries' prowess declined early in the 17th century as troop standards dropped and the drill was abandoned. According to the author of The Laws of the Janissaries (Kavanin-i Yenigeriyan), by 1606 members of the Janissaries were faced with supply issues so that they "were no longer given powder for the drills and that the soldiers used the wick for their candles and not for their muskets."[14]
In 1548 the Ming started producing their own arquebuses after procuring knowledge of the weapon from the pirate network at Shuangyu Harbor (雙嶼港).[15] The military leader Qi Jiguang in particular realized the vital role of this new weapon in combating piracy, for it out ranged their heaviest arrows, and sought to incorporate them into his troops. By 1560 he had invented a style of musket warfare similar to the countermarch which he described the same year:
All the musketeers, when they get near the enemy are not allowed to fire early, and they're not allowed to just fire everything off in one go, [because] whenever the enemy then approaches close, there won't be enough time to load the guns (銃裝不及), and frequently this mismanagement costs the lives of many people. Thus, whenever the enemy gets to within a hundred paces' distance, they [the musketeers] are to wait until they hear a blast on the bamboo flute, at which they deploy themselves in front of the troops, with each platoon (哨) putting in front one team (隊). They [the musketeer team members] wait until they hear their own leader fire a shot, and only then are they allowed to give fire. Each time the trumpet gives a blast, they fire one time, spread out in battle array according to the drilling patterns. If the trumpet keeps blasting without stopping, then they are allowed to fire all together until their fire is exhausted, and it's not necessary [in this case] to divide into layers.[16]— Ji xiao xin shu Tonio Andrade translation
In another passage he elaborates on his style of musket formation using layered musket volleys: "Once the enemy has approached to within 100-paces, listen for one's own commander (總) to fire once, and then each time a horn is blown the arquebusiers fire one layer. One after another, five horn tones, and five layers fire. Once this is done, listen for the tap of a drum, at which then one platoon (哨) [armed with traditional weapons] comes forward, proceeding to in front of the arquebusiers. They [the platoon members] then listen for a beat of the drum, and then the blowing of the swan-call horn, and they then give a war cry and go forth and give battle."[16] If melee weapons could not be brought into combat, such as during long range defense, Qi recommended waiting "until the face-the-enemy signal [is given], and then, whether from behind wooden stockades, or from moat banks, or from below abatis (拒馬), [they] open up on the enemy, firing by turns (更番射賊). Those who are empty reload; those who are full fire again. While the ones who have fired are loading, those who are full then fire again. In this way, all day long, the firing of guns will not be lacking, and there must be no firing to the point of exhaustion [of ammo] and no slipups with guns."[17] In 1571 Qi prescribed an ideal infantry regiment of 1080 arquebusiers out of 2700 men, or 40 percent of the infantry force. However it is not known how well this was actually implemented, and there is evidence that Qi was met with stiff resistance to the incorporation of newer gunpowder weapons in northern China while he was stationed there.[18] He writes that "in the north soldiers are stupid and impatient, to the point that they cannot see the strength of the musket, and they insist on holding tight to their fast lances (a type of fire lance), and although when comparing and vying on the practice field the musket can hit the bullseye ten times better than the fast-lance and five times better than the bow and arrow, they refuse to be convinced."[18]
The countermarch volley may have been used in Japan as well as early as 1575 at the Battle of Nagashino by Oda Nobunaga's arquebusiers.[19] But this has been called into dispute in recent years by J.S.A. Elisonas and J.P. Lamers in their translation of The Chronicle of Oda Nobunaga by Ota Gyuichi. In Lamers' Japonius he says that "whether or not Nobunaga actually operated with three rotating ranks cannot be determined on the basis of reliable evidence."[20] They claim that the version of events describing volley fire was written several years after the battle, and an earlier account says to the contrary that guns were fired en masse.[21] However both Korean and Chinese sources note that Japanese gunners were making use of volley fire during the Japanese invasions of Korea from 1592–98.[22]
European gunners might have implemented the volley fire to some extent since at least 1579 when the Englishman Thomas Digges suggested that musketeers should, "after the old Romane manner make three or four several fronts, with convenient spaces for the first to retire and unite himselfe with the second, and both these if occasion so require, with the third; the shot [musketeers] having their convenient lanes continually during the fight to discharge their peces."[23] The Spanish too displayed some awareness of the volley technique and described it in a military manual dating to 1586: "Start with three files of five soldiers each, separated one from the other by fifteen paces, and they should comport themselves not with fury but with calm skillfulness [con reposo diestramente] such that when the first file has finished shooting they make space for the next (which is coming up to shoot) without turning face, countermarching [contrapassando] to the left but showing the enemy only the side of their bodies, which is the narrowest of the body, and [taking their place at the rear] about one to three steps behind, with five or six pellets in their mouths, and two lighted matchlock fuses … and they load [their pieces] promptly … and return to shoot when it's their turn again."[24] There is also some slight evidence that a form of volley fire might have been employed by Prospero Colonna's arquebusiers as early as the Battle of Bicocca (1522).[25] However this has generally been panned by historians as both an over interpretation as well as mis-citation of a passage by Charles Oman suggesting that the Spanish arquebusiers kneeled to reload, when in fact Oman never made such a claim.[26]
Regardless, it is clear that the concept of volley fire had existed in Europe for quite some time during the 16th century, but it was in the Netherlands during the 1590s that the musketry volley really took off. The key to this development was William Louis, Count of Nassau-Dillenburg who in 1594 described the technique in a letter to his cousin:
I have discovered … a method of getting the musketeers and soldiers armed with arquebuses not only to keep firing very well but to do it effectively in battle order … in the following manner: as soon as the first rank has fired together, then by the drill [they have learned] they will march to the back. The second rank, either marching forward or standing still, [will next] fire together [and] then march to the back. After that, the third and following ranks will do the same. Thus before the last ranks have fired, the first will have reloaded.[27]— Letter from Louis to Maurice
For many Europeans this new way of conducting warfare seemed ridiculous, so that in the beginning their practitioners were openly mocked. But the Dutch army continued to drill the volley under both Louis and his cousin Maurice, Prince of Orange, so that it became second nature. One Dutch historian recounts the exercises in which regiments marched "man by man bringing the rearmost to the front and the frontmost to the rear.… The beginnings were very difficult, and many people felt, because it was all so unusual, that it was odd and ridiculous [lacherlich]. They were mocked by the enemy, but with time the great advantages of the practices became clear … and eventually they were copied by other nations."[28] Soon the reorganized Dutch army displayed the virtues of the countermarch volley and the practice spread across Europe. An important component to the successful deployment of volley fire was the drill, which according to Geoffrey Parker, "Only two civilisation have invented drill for their infantry: China and Europe. Moreover, both of them did so twice: in the fifth century BC in North China and in Greece, and again in the late sixteenth century. Exponents of the second phase— Qi Jiguang in Imperial China and Maurice of Nassau in the Dutch Republic— explicitly sought to revive classical precedents, and in the West, marching in step and standing on parade became a permanent part of military life."[29] Drill was difficult and the manner in which the volley fire should be executed had not been perfected in Louis' time. It is clear from Holland's historical sources that it took many trials and experiments for the process to be refined.[23]
Indeed the musketry volley drills seemed so unorthodox to some that in some parts of the world there was a push back against the incorporation of muskets themselves. According to Qi Jiguang, this was because:
The musket was originally considered a powerful weapon, and in attacking the enemy is one that has been much relied upon. But how is it that so many officers and soldiers don't think it can be relied upon heavily? The answer lies in the fact that in drills and on the battlefield, when all the men fire at once, the smoke and fire settle over the field like miasmal clouds, and not a single eye can see, and not a singe hand can signal. Not all [soldiers] hold their guns level, or they don't hold them to the side of their cheek, or they don't use the sights, or they let their hands droop and support it to hold it up, and one hand holds the gun and one hand uses the fuse to touch off the fire, thus failing to use the matchlock grip— what of them? It's just a case of being out of practice and uncourageous, hurrying but not being able to take out the fire fuse and place it in the matchlock grip, trying for speed and convenience. In this way, there is absolutely no way to be accurate, and so how could one value muskets? Especially given that the name of the weapon is "bird-gun," which comes from the way that it can hit a flying bird, hitting accurately many times. But in this way, fighting forth, the power doesn't go the way one intends, and one doesn't know which way it goes— so how can one hit the enemy, to say nothing of being able to hit a bird?[30]— Ji xiao xin shu
In Korea the Joseon dynasty underwent a devastating war with newly unified Japan that lasted from 1592 to 1598. The shock of such an encounter spurred the court to undergo a military strengthening process. One of the core elements of the movement was to adopt the musket. According to the reformers, "In recent times in China they did not have muskets; they first learned about them from the Wokou pirates in Zhejiang Province. Qi Jiguang trained troops in their use for several years until they [muskets] became one of the skills of the Chinese, who subsequently used them to defeat the Japanese."[31] By 1607 Korean musketeers had been trained in the fashion which Qi Jiguang prescribed, and a drill manual had been produced based on the Chinese leader's Ji xiao xin shu. Of the volley fire, the manual says that "every musketeer squad should either divide into two musketeers per layer or one and deliver fire in five volleys or in ten."[31] Another Korean manual produced in 1649 describes a similar process: "When the enemy approaches to within a hundred paces, a signal gun is fired and a conch is blown, at which the soldiers stand. Then a gong is sounded, the conch stops blowing, and the heavenly swan [a double-reed horn] is sounded, at which the musketeers fire in concert, either all at once or in five volleys (齊放一次盡擧或分五擧)."[31] This training method proved to be quite formidable in the 1619 Battle of Sarhu when 10,000 Korean musketeers managed to kill many Manchus before their allies surrendered. While Korea went on to lose both wars against the Manchu invasions of 1627 and 1636, their musketeers were well respected by Manchu leaders. It was the first Qing emperor Hong Taiji who wrote: "The Koreans are incapable on horseback but do not transgress the principles of the military arts. They excel at infantry fighting, especially in musketeer tactics."[32]
In the 18th century, the British would use volley fire to make up for the inaccuracy and limited range (100 yards) of their musket, the Brown Bess. Armies approached one another in linear formations. British soldiers would fire volleys in the general direction of the enemy, by ranks. The command they were given was to level weapons, rather than to aim.[33] The shooters might be formed in three ranks, with the front rank firing simultaneously, then the second rank, offset, then the third, after which the first rank was ready to fire again.[34] The Austrian Empire, and later the Austro-Hungarian Empire, had much trouble trying to implement the tactic. It was soon abandoned after many embarrassing losses. Effective volley fire required practice in swiftly completing the required motions.[35] In the American Civil War volley fire was used quite effectively, since the effective range and rate of fire were greater than in earlier centuries.[34]
Depictions
Volley fire in film was depicted in the Movie Zulu recounting the Battle of Rorke's Drift. In the defense of a fixed position, British infantry utilized a three rank volley fire to decimate an attack by a large Zulu force. Despite the Zulu's superior numbers, their attack collapsed under the relentless volley fire they faced.
Volley fire by the British Army was depicted in the movie The Patriot
In modern times
In modern times the use of volley fire is limited, since automatic weapons can devastate massed infantry on their own without volley fire formations.
Citations
- ↑ Andrade 2016, p. 144.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Andrade 2016, p. 149.
- 1 2 3 4 Andrade 2016, p. 150.
- 1 2 Andrade 2016, p. 149-150.
- 1 2 Andrade 2016, p. 152.
- ↑ Andrade 2016, p. 153-154.
- 1 2 Andrade 2016, p. 154.
- ↑ Andrade 2016, p. 155.
- ↑ Villalon 2008, p. 75.
- 1 2 Andrade 2016, p. 157.
- 1 2 3 4 Andrade 2016, p. 158.
- ↑ Andrade 2016, p. 158-159.
- 1 2 Andrade 2016, p. 159.
- 1 2 3 4 Ágoston 2008, p. 24.
- ↑ Andrade 2016, p. 171.
- 1 2 Andrade 2016, p. 173.
- ↑ Andrade 2016, p. 174.
- 1 2 Andrade 2016, p. 178-179.
- ↑ Andrade 2016, p. 169.
- ↑ Andrade 2016, p. 354.
- ↑ Andrade 2016, p. 170.
- ↑ Andrade 2016, p. 181.
- 1 2 Andrade 2016, p. 147.
- ↑ Andrade 2016, p. 146.
- ↑ Eltis 1998, p. 31
- ↑ Andrade 2016, p. 350.
- ↑ Andrade 2016, p. 145.
- ↑ Andrade 2016, p. 145-6.
- ↑ Andrade 2016, p. 148.
- ↑ Andrade 2016, p. 178-9.
- 1 2 3 Andrade 2016, p. 183.
- ↑ Andrade 2016, p. 186.
- ↑ Dickinson, H.T., "A companion to eighteenth-century Britain," Wiley-Blackwell, 2002. Page 479. ISBN 978-0-631-21837-1 Retrieved September 28, 2011
- 1 2 McKay, John, Bradford, James C., and Pawlowsky, Rebeccah, "The big book of Civil War sites," Globe Pequot, 2011. ASIN: B004EWGS3S Page 432. Retrieved September 28, 2011.
- ↑ Gilbert, Adrian "The encyclopedia of warfare: from earliest times to the present day," Lyons Press, 2003. Page 76. ISBN 978-1-59228-027-8 Retrieved September 28, 2011
References
- Ágoston, Gábor (2008), Guns for the Sultan: Military Power and the Weapons Industry in the Ottoman Empire, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 0521603919
- Andrade, Tonio (2016), The Gunpowder Age: China, Military Innovation, and the Rise of the West in World History, Princeton University Press, ISBN 9781400874446
- Villalon, L. J. Andrew (2008), The Hundred Years War (part II): Different Vistas, Brill Academic Pub, ISBN 978-90-04-16821-3