World economy
| Statistics | |
|---|---|
| Population | 7.095 billion (July 2013 est.)[1] |
| GDP |
Nominal: $77.609 trillion (2014 est.)[1] PPP: $106.998 trillion (2014 est.)[1] |
GDP growth | 3.4% (2014)[2] |
GDP per capita |
Nominal: $10,857 PPP: $15,073 (2014 est.) |
|
~10 million i.e. ~0.15% (2009) | |
| Billionaires | 1,594 (2014) [3] |
| People earn below $2 per day | ~3.25 billion (~50%) |
| Unemployment |
5.4% (Nov.2014)[4] note: 30% combined unemployment and underemployment in many non-industrialized countries; developed countries typically 4%–12% unemployment (2007 est.) |
|
Trailing-ten-years. Some numbers exclude certain countries for lack of information. All values, unless otherwise stated, are in US dollars. | |
| World economy |
|---|
The world economy or global economy is the economy of the world, considered as the international exchange of goods and services that is expressed in monetary units of account (money).[5] In some contexts, the two terms are distinguished: the "international" or "global economy" being measured separately and distinguished from national economies while the "world economy" is simply an aggregate of the separate countries' measurements. Beyond the minimum standard concerning value in production, use, and exchange the definitions, representations, models, and valuations of the world economy vary widely. It is inseparable from the geography and ecology of Earth.
It is common to limit questions of the world economy exclusively to human economic activity, and the world economy is typically judged in monetary terms, even in cases in which there is no efficient market to help valuate certain goods or services, or in cases in which a lack of independent research or government cooperation makes establishing figures difficult. Typical examples are illegal drugs and other black market goods, which by any standard are a part of the world economy, but for which there is by definition no legal market of any kind.
However, even in cases in which there is a clear and efficient market to establish a monetary value, economists do not typically use the current or official exchange rate to translate the monetary units of this market into a single unit for the world economy, since exchange rates typically do not closely reflect worldwide value, for example in cases where the volume or price of transactions is closely regulated by the government.
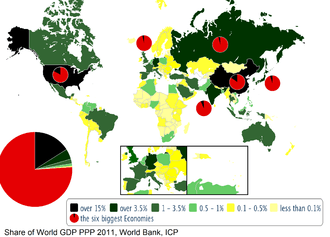
Rather, market valuations in a local currency are typically translated to a single monetary unit using the idea of purchasing power. This is the method used below, which is used for estimating worldwide economic activity in terms of real US dollars or euros. However, the world economy can be evaluated and expressed in many more ways. It is unclear, for example, how many of the world's 7.13 billion people have most of their economic activity reflected in these valuations.
As of 2015, the following 13 countries or regions have reached an economy of at least US$2 trillion by GDP in nominal or PPP terms: Brazil, China, France, Germany, India, Indonesia, Italy, Japan, Mexico, Russia, the United Kingdom, the United States, and the European Union.[7]
Economy – overview
World economy by Country Groups
The following two tables list the Country Groups with individual countries designated by the IMF.[8] Members of the G-20 major economies are in bold.
| List of Country Groups by GDP (nominal) in 2014 in Billions US$[9] | List of Country Groups by GDP (PPP) in 2015 in Billions US$[9] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Current world economic league table of largest economies in the world by GDP and share of global economic growth
The following two tables list the twenty largest economies by GDP (Nominal), twenty largest economies by GDP (PPP), and the twenty economies with the largest shares of global economic growth from 2014 to 2015. Members of the G-20 major economies are in bold.
| List of the 25 largest economies by GDP (nominal) at their peak level of GDP in Billions US$[9][10] |
List of the 25 largest economies by GDP (PPP) at their peak level of GDP in Billions US$[9][11] |
List of the 10 largest economies by contribution to global economic growth by GDP (nominal) over 2014-15[12] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Twenty Largest Economies in the World by Nominal GDP
The following is a list of the twenty largest economies by nominal GDP at a specific year according to International Monetary Fund.[13]
Twenty Largest Economies in the World by PPP GDP (IMF and CIA World Factbook)
The following is a list of twenty largest economies by GDP (PPP) at a specific year according to the CIA World Factbook and the International Monetary Fund.[14][15]
Statistical indicators
Economy
- GDP (GWP) (gross world product): (purchasing power parity exchange rates) – $59.38 trillion (2005 est.), $51.48 trillion (2004), $23 trillion (2002)
- GDP (GWP) (gross world product):[16] (market exchange rates) – $60.69 trillion (2008)
- GDP – real growth rate: 3.2% (2008), 3.1% p.a. (2000–07), 2.4% p.a. (1990–99), 3.1% p.a. (1980–89)
- GDP – per capita: purchasing power parity – $9,300, €7,500 (2005 est.), $8,200, €6,800 (92) (2003), $7,900, €5,000 (2002)
- World median income: purchasing power parity $1,041, €950 (1993)[17]
- GDP – composition by sector: agriculture: 4%; industry: 32%; services: 64% (2004 est.)
- Inflation rate (consumer prices): developed countries 1% to 4% typically; developing countries 5% to 60% typically; national inflation rates vary widely in individual cases, from declining prices in Japan to hyperinflation in several Third World countries (2003)
- Derivatives OTC outstanding notional amount: $601 trillion (Dec 2010) ()
- Derivatives exchange traded outstanding notional amount: $82 trillion (June 2011) ()
- Global debt issuance: $5.187 trillion, €3 trillion (2004), $4.938 trillion, €3.98 trillion (2003), $3.938 trillion (2002) (Thomson Financial League Tables)
- Global equity issuance: $505 billion, €450 billion (2004), $388 billion. €320 billion (2003), $319 billion, €250 trillion (2002) (Thomson Financial League Tables)
Employment
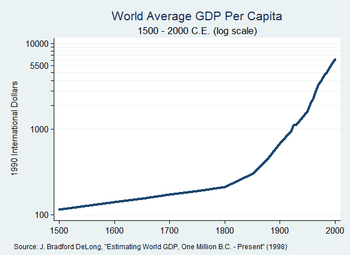
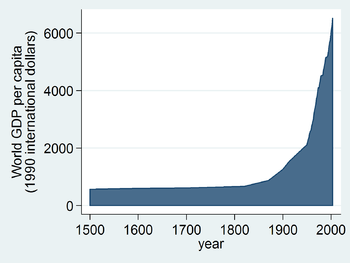
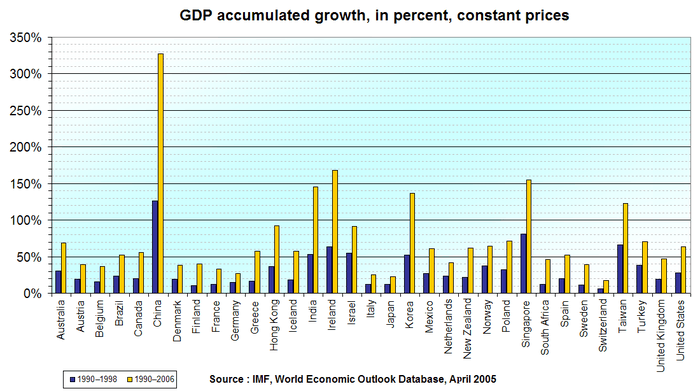
- Unemployment rate: 8.7% (2009 est.). 30% (2007 est.) combined unemployment and underemployment in many non-industrialized countries; developed countries typically 4%–12% unemployment.
Industries
- Industrial production growth rate: 3% (2002 est.)
Energy
- Yearly electricity – production: 21,080,878 GWh (2011 est.),[18] 15,850,000 GWh (2003 est.), 14,850,000 GWh (2001 est.)
- Yearly electricity – consumption: 14,280,000 GWh (2003 est.), 13,930,000 GWh (2001 est.)
- Oil – production: 79,650,000 bbl/d (12,663,000 m3/d) (2003 est.), 75,460,000 barrels per day (11,997,000 m3/d) (2001)
- Oil – consumption: 80,100,000 bbl/d (12,730,000 m3/d) (2003 est.), 76,210,000 barrels per day (12,116,000 m3/d) (2001)
- Oil – proved reserves: 1.025 trillion barrel (163 km³) (2001 est.)
- Natural gas – production: 3,366 km³ (2012 est.),[19] 2,569 km³ (2001 est.)
- Natural gas – consumption: 2,556 km³ (2001 est.)
- Natural gas – proved reserves: 161,200 km³ (1 January 2002)
Cross-border
- Yearly exports: $12.4 trillion, €11.05 trillion (2009 est.)
- Exports – commodities: the whole range of industrial and agricultural goods and services
- Exports – partners: US 12.7%, Germany 7.1%, China 6.2%, France 4.4%, Japan 4.2%, UK 4.1% (2008)
- Yearly imports: $12.29 trillion, €10.95 trillion (2009 est.)
- Imports – commodities: the whole range of industrial and agricultural goods and services
- Imports – partners: China 10.3%, Germany 8.6%, US 8.1%, Japan 5% (2008)
- Debt – external: $56.9 trillion, €40 trillion (31 December 2009 est.)
Gift economy
- Yearly economic aid – recipient: net Official Development Assistance (ODA) of $135.2 billion (2014)[20]
Communications
Telephones – main lines in use: 843,923,500 (2007)
4,263,367,600 (2008)
- Telephones – mobile cellular: 3,300,000,000 (Nov. 2007)[21]
- Internet Service Providers (ISPs): 10,350 (2000 est.)
- Internet users: 3,079,339,857 (December 31, 2014 ), 360,985,492 (December 31, 2000[22])
Transport
Transportation infrastructure worldwide includes:
- Airports
- Total: 41,821 (2013)[23]
- Roadways (in kilometres)
- Total: 32,345,165 km
- Paved: 19,403,061 km
- Unpaved: 12,942,104 km (2002)
- Railways
- Total: 1,122,650 km includes about 190,000 to 195,000 km of electrified routes of which 147,760 km are in Europe, 24,509 km in the Far East, 11,050 km in Africa, 4,223 km in South America, and 4,160 km in North America.
Military
- World military expenditure in 2012: estimated to $1.756 trillion [24]
- Military expenditures – percent of GDP: roughly 2% of gross world product (1999).
Economic studies
To promote exports, many government agencies publish on the web economic studies by sector and country. Among these agencies include the USCS (US DoC) and FAS (USDA) in the United States, EDC and AAFC in Canada, Ubifrance in France, UKTI in the UK, HKTDC and JETRO in Asia, Austrade and NZTE in Oceania. Through Partnership Agreements, The Federation of International Trade Associations publishes studies from several of these agencies (USCS, FAS, AAFC, UKTI, HKTDC), as well as other non-governmental organizations on its website GlobalTrade.net.
See also
- Economic history of the world
- Common Wealth: Economics for a Crowded Planet (book)
- Global workforce
- Globality
- Globalization
- Global financial system
- Trade route
- World Trade Report
- Emerging and growth-leading economies
Regional economies:
- Economy of Africa
- Economy of Asia
- Economy of Europe
- Economy of North America
- Economy of Oceania
- Economy of South America
Events:
Lists:
- List of countries by GDP sector composition
- List of world's largest economies (nominal) – based on current currency market exchange rates
- List of world's largest economies (PPP) – based on purchasing power parity
- Historical list of world's largest economies (nominal) – for the years between 1998 and 2003
- Historical list of world's largest economies (PPP) – for the years between 1 and 1998
- List of world production
References
- 1 2 3 "IMF". imf.org. Retrieved 2014-10-10.
- ↑ "World Economic Outlook (WEO), April 2015, Chapter 1" (PDF). IMF. April 2015. Retrieved 2015-06-15.
- ↑ "Forbes". http://www.forbes.com/billionaires/list. Forbes. External link in
|website=(help); - ↑ "BLS". http://www.bls.gov/bls/newsrels.htm#major. BLS. External link in
|website=(help); - ↑ "World Economy." - Definition. American English Definition of with Pronunciation by Macmillan Dictionary. N.p., n.d. Web. 02 Jan. 2015.
- ↑ http://siteresources.worldbank.org/ICPEXT/Resources/ICP_2011.html
- ↑ "Gross domestic product, current prices & Gross domestic product based on purchasing-power-parity (PPP) valuation of country GDP". World Economic Outlook Database, October 2015. International Monetary Fund. October 2015. Retrieved 2015-10-15.
- ↑ IMF GDP 2014 Data (October 2015)
- 1 2 3 4 "Gross domestic product". IMF World Economic Outlook. April 2016. Retrieved 14 April 2016.
- ↑ IMF GDP (Nominal) Data (October 2015)
- ↑ IMF GDP (PPP) Data (October 2015)
- ↑ IMF GDP (nominal) 2014 and 2015 Data (October 2015)
- ↑ "Gross domestic product, current prices". International Monetary Fund. International Monetary Fund. October 2015. Retrieved 11 October 2015.
- ↑ "Gross domestic product based on purchasing-power-parity (PPP) valuation of country GDP; Current international dollar". International Monetary Fund. October 2015. Retrieved 11 October 2015.
- ↑ "GDP (PURCHASING POWER PARITY)". CIA World Factbook. CIA World Factbook. 2014. Retrieved October 7, 2014.
- ↑ "IMF World Economic Outlook, Crisis and Recovery, April 2009". Imf.org. 2009-04-16. Retrieved 2012-07-17.
- ↑ B. Milanovic (January 2002). "True World Income Distribution, 1988 and 1993: First Calculation Based on Household Surveys Alone" (PDF). Retrieved 13 May 2011.
- ↑ http://www.eia.gov/cfapps/ipdbproject/IEDIndex3.cfm?tid=2&pid=2&aid=12
- ↑ http://www.eia.gov/cfapps/ipdbproject/iedindex3.cfm?tid=3&pid=3&aid=1&cid=regions&syid=2008&eyid=2012&unit=BCF
- ↑ "Development aid stable in 2014 but flows to poorest countries still falling". OECD. 2015-04-08. Retrieved 2015-07-23.
- ↑ global cellphone penetration reaches 50 percent
- ↑ "World Internet Usage Statistics News and World Population Stats". Internetworldstats.com. Retrieved 2015-06-08.
- ↑ https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/fields/2053.html
- ↑ http://www.sipri.org/yearbook/2013/03
External links
| Wikiquote has quotations related to: World economy |
- OECD – Economic Outlook
- - US Bureau of Labor and Statistics, Nov.2014 Unemployment Numbers
- IMF – World Economic Outlook
- UN DESA – World Economy publications
- CIA – The World Factbook – World
- Career Education for a Global Economy
- BBC News Special Report – Global Economy
- Guardian Special Report – Global Economy
- World Bank Summary Trade Statistics for World