Amissville, Virginia
| Amissville | |
|---|---|
| Unincorporated community | |
|
View of Amissville, along Route 211 (facing west) | |
 Amissville  Amissville Location within the state of Virginia | |
| Coordinates: 38°40′17″N 77°59′44″W / 38.67139°N 77.99556°WCoordinates: 38°40′17″N 77°59′44″W / 38.67139°N 77.99556°W | |
| Country | United States |
| State | Virginia |
| County | Rappahannock |
| Time zone | Eastern (EST) (UTC-5) |
| • Summer (DST) | EDT (UTC-4) |
Amissville is an unincorporated community in Rappahannock County in the U.S. state of Virginia. It is located on U.S. Route 211 about halfway between Warrenton and the small town of Washington, Virginia.
The Locust Grove/R.E. Luttrell Farmstead and Meadow Grove Farm are listed on the National Register of Historic Places.[1]
History
Amissville was first settled by French Huguenots and the English. In about 1763, Thomas Fairfax, 6th Lord Fairfax of Cameron granted tracts of land to Joseph Bayse and Joseph Amiss. Joseph Amiss distributed his land among his four sons, William, Gabriel, Philip, and Thomas. The Amissville post office was established on October 2, 1810, with Thomas Amiss acting as its first postmaster. The area was still largely inhabited by the Amiss and Bayse families, and both families wanted the town to be named in their own honor. An election was held, and by a one vote margin it became Amissville and not Bayseville.
In an 1855 gazetteer, it was described as "a small post-village" with "about 75 inhabitants, including surnames such as Amiss, Bayse, Poe, Corbin, Laing, Luttrell, Bywaters, Riley, Pickett, Hackley, Corder, and Smith."[2]
Civil War
Amissville is near the site of a minor action on July 24, 1863, involving George A. Custer's Michigan Brigade of cavalry following the Confederate loss at Gettysburg. Longstreet's corps and Gen. A. P. Hill's corps were retreating from Pennsylvania through the Chester Gap and south on the Richmond Road towards Culpeper. Custer and his troops traveled from their headquarters and camp near Amissville and attacked with cavalry and artillery from the southern slope of Battle Mountain (about 5 miles southwest of the village), but his forces were vastly outnumbered and after a brisk and severe fight, forced to retreat north and east over Battle Mountain back to Amissville. Two of Custer's men were awarded the Medal of Honor in 1893 for their part in capturing Confederate artillery at Battle Mountain. Battle Mountain and Little Battle Mountain were named not for the military engagement but for the Bataille family which lived near the two elevations in the 1700s. Bataille was later corrupted to Battle Mountain and Little Battle Mountain, the names they bear today.
Amissville was also the site of a sharp cavalry fight in November 1862, at Corbin's Crossroads, when Gen. J.E.B. Stuart's Confederate cavalry were heading to Culpeper County following the Battle of Antietam in Maryland. At Corbin's crossroads, during the fight, Gen. Stuart narrowly escaped death when he turned his head and an Union bullet clipped off half of his moustache. The site of the engagement is about 3/4 of a mile south of the present village of Amissville.
In late August 1862, Gen. Stuart and his cavalry were scouting around Maj. Gen. John Pope's Federal Army of Virginia, elements of which were moving towards Thoroughfare Gap in Fauquier County. Gen. Stuart and his cavalry reached Amissville on August 22, and turned back to surround Pope's army. In an attack near Catlett's Station, Gen. Stuart's men captured Gen. Pope's overcoat and military papers.
Climate
The climate in this area is characterized by hot, humid summers and generally mild to cool winters. According to the Köppen Climate Classification system, Amissville has a humid subtropical climate, abbreviated "Cfa" on climate maps.[3]
Geology
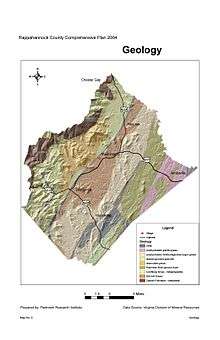
The geology of Amissville and the surrounding vicinity consists of several units. Predominant and oldest (approximately 704 million years old, +/- 5 million years, based on the U-Pb zircon geochronology dating method, coinciding with the initial rifting of the supercontinent Rodinia) is the Neoproterozoic alkali feldspar granitic rock of the Robertson River Igneous Suite.[4] This includes felsic complex material such as biotite, hornblende-biotite, magnetite, and alkali granitic rock including rhyolite on the eastern slopes of Battle Mountain[5] and Little Battle Mountain.


Battle Mountain and Little Battle Mountain are the only mountains in Rappahannock County which are known to be volcanic in origin, and are among the oldest visibly intact extinct volcanoes in Virginia. White quartz boulders and smaller fragments are common on and around Battle Mountain, a result of molten silica that was contained in the rhyolite lava and granitic magma that formed the volcano.

The Robertson River Igneous Suite extends from south of Laurel Mills (originating near Charlottesville) and runs north-northeast through Hackleys Crossroad and beyond in a band approximately four kilometers wide. Precambrian coarse leucogneiss and fine-grained gneiss prevails from the eastern edge of the Amissville, Rappahannock County area from north of the Amissville post office and U.S. Route 211 and south to Viewtown. Flint Hill Gneiss, a light to dark-gray quartz monzonite gneiss is predominate from Ben Venue and west to Massies Corner and extending further into Rock Mills and the town of Washington, Virginia.
A fine-grained Precambrian arkosic sandstone and conglomerate, which Aaron Mountain is composed of, occurs on the contact between the Flint Hill Gneiss starting approximately two kilometers west of Laurel Mills and running north-northeast along a narrow band (starting out at approximately 1 kilometer wide and tapering down to 100 meters) in contact with the Robertson River Igneous Suite, terminating just south of U.S. Route 211. The creeksides and river bottoms of the Thorton River, Battle Run and the Rappahannock River and their smaller tributaries are all composed of Quaternary Period alluvium including stratified, unconsolidated gray to grayish-yellow sand, silt and local gravels.[6]
References
- ↑ National Park Service (2010-07-09). "National Register Information System". National Register of Historic Places. National Park Service.
- ↑ {{cite book|last=Edwards|first=Richard|title=Statistical Gazetteer of the State of Virginia|date=1855|publisher=Richard Edwards|location=Richmond, Virginia|page=165|url=https://archive.org/details/statisticalgazet00edwa}}
- ↑ Climate Summary for Amissville, Virginia
- ↑ Richard P. Tollo and Sara Arav (1992). "The Robertson River Igneous Suite (Blue Ridge Province, Virginia)—Late Proterozoic anorogenic (A-type) granitoids of unique petrochemical affinity. Basement Tectonics 8 (pp. 425–441).". Springer Netherlands. Retrieved 2016-08-07.
- ↑ Thomas A. Woolman (April 1, 2016). "A Gallium Anomaly Utilized in Palaeogeographic Reconstruction of Battle Mountain, Rappahannock County, Virginia". Kansas Academy of Science. Retrieved 2016-07-14.
- ↑ Michael T. Lukert and Christopher R. Hallady (1980). "Geology of the Massies Corner Quadrangle, Virginia". Virginia Department of Mines, Minerals and Energy. Retrieved 2016-08-05.