Bluemont, Virginia
| Bluemont, Virginia | |
|---|---|
| Unincorporated community | |
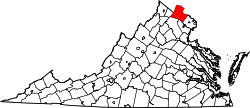
 Bluemont, Virginia  Bluemont, Virginia  Bluemont, Virginia Location within the state of Virginia | |
| Coordinates: 39°6′40″N 77°50′2″W / 39.11111°N 77.83389°WCoordinates: 39°6′40″N 77°50′2″W / 39.11111°N 77.83389°W | |
| Country |
|
| State |
|
| County |
|
| Time zone | Eastern (EST) (UTC-5) |
| • Summer (DST) | EDT (UTC-4) |
Bluemont is an unincorporated community village in Loudoun County, Virginia located at the base of Snickers Gap in the Blue Ridge Mountain. As of 2010, the Bluemont postal area had a population of 2,834. At 680 feet (210 m), it is the highest community in Loudoun County. Originally named Snickersville, Bluemont changed its name to attract Washingtonians out to it when a predecessor of the Washington and Old Dominion Railroad was extended to the town from Round Hill. It is located on Virginia Route 7 just west of the incorporated town of Round Hill. Every fall it is home to the Bluemont Fair.
A nearby landmark is Mount Weather, an operations and training facility above ground for the Federal Emergency Management Agency and is rumored to contain an underground facility designed to house or replace the American government in the case of nuclear warfare.
History
The settlement of the area that is now Bluemont began in the 1770s when a connection was made between the old Winchester Pike, which led from Loudoun to Winchester via Keyes' (Vestals) Gap, and the Colchester Road which ran from the port of Colchester to Winchester via Snickers Gap (named after Edward Snickers, who operated a ferry across the nearby Shenandoah River).[1]
The new connector road greatly reduced the distance one had to travel to get to Winchester from points east along the Winchester Pike and quickly became widely used. At the intersection of these two roads (present day Clayton Hall Road and Snickersville Turnpike) a small village began to develop, centered around the home of William Clayton, Clayton Hall, and the dependencies he built for his farm at the gap. The village was christened Snickers' Gap in 1807 when a post office was established there.
17 years later, in 1826, the town was incorporated by the General Assembly as Snickersville, though it would take another six years for the post office there to change its name. The completion of the Leesburg and Snickers Gap Turnpike in 1832 (present day Virginia State Highway 7) brought new prosperity and prestige to the village, and the last major growth it would see for the next half-century. Despite the strategic importance of Snickers' Gap during the Civil War the village saw surprisingly little action save the coming and going of the armies through the gap. The only major action in the town was one of 8 small partisan skirmishes in the area which took place May 23, 1864, when 14 Confederates surprised and routed 22 Federals resting on the village.
In 1875, the Washington and Ohio Railroad, which began in Alexandria, was extended to Round Hill. The lure of the Blue Ridge some four miles west prompted a livery service to run from Snickersville to Round Hill to pick up travelers and take to them to one of the several hotels that began to spring up in and about the town. By 1900, the success of the resorts in the vicinity of Snickersville, including Jules DeMonet's Blue Ridge Inn at Bear's Den, prompted the Southern Railway (which had acquired the Washington & Ohio's route) to extend its tracks to the town, which became the final western terminus of line. The extension permitted the steam railroad's passengers to travel to the base of the Blue Ridge from a terminal in Washington, D.C.
To promote the resort nature of the town, the railroad petitioned the United States Postal Service to change the name of the town to Bluemont. The Postal Service acquiesced to this request on September 7, 1900. The zenith of the town came in 1908, when its population peaked at 200.
In 1912, interurban electric trolleys of the new Washington and Old Dominion Railway began to serve Bluemont on the Southern Railway's former steam route. However, with the advent of the automobile, the rail based tourism that was so good to the town began to decline. In 1939, deteriorating conditions on a trestle immediately east of Round Hill, combined with a lack of rail traffic, led to the abandonment of the line between Purcellville and Bluemont.
By the 1940s Bluemont had become a sleepy village of about 140 inhabitants. Still its scenic location continued to be a lure, especially artists and musicians, including artist Clyde Beck, who with Evelyn Johnson, founded the Bluemont Citizens Association and the annual Bluemont Fair in 1968. Around the same time the commune of Skyfields was established by local musicians Howard Bass and Peter Dunning. From the commune and the musicians it attracted was founded the Bluemont Concert Series in the 1970s.
In 1984, the Bluemont Historic District was listed on the National Register of Historic Places.[2][3] A historic marker at the intersection of Clayton Hall Road and Snickersville Turnpike identifies the location of the Historic District, which is a Virginia Historic Landmark.[4] The Bear's Den Rural Historic District was listed in 2008.[5]
As of 2007, the village has about 200 residents. The Bluemont ZIP code (20135) encompasses parts of three counties and two states (Loudoun County, Virginia; Clarke County, Virginia; and Jefferson County, West Virginia).
Bluemont Fair
The Bluemont Fair is held annually on the third weekend in September. It features juried crafters, a pickle and pie contest, a 10K race, and live music in a variety of styles. While the fair is spread throughout the village, the primary site is the grounds of the Bluemont Community Center at the eastern edge of the village.
Sponsored by the Bluemont Citizens Association, the proceeds from the fair are used to fund street lighting, local student scholarships, community beautification, historic building improvements within the village and to support local service organizations.
Painter William D. Washington was born in Bluemont when it was still known as Snickersville.
Newspapers
- Purcellville Gazette Newspaper[6]
Climate
The climate in this area is characterized by hot, humid summers and generally mild to cool winters. According to the Köppen Climate Classification system, Bluemont has a humid subtropical climate, abbreviated "Cfa" on climate maps.[7]
Bibliography
- Scheel, Eugene (2002). Quaker Country and the Loudoun Valley. Loudoun Discovered: Communities, Corners and Crossroads. 4. Leesburg, Virginia: The Friends of the Thomas Balch Library.
References
- ↑ Snickersville Dot Com
- ↑ National Register of Historic Places nomination form for Bluemont Historic District in official website of the Virginia Department of Historic Resources Accessed 29-Oct-2008.
- ↑ List of Virginia properties on National Register of Historic Places in official website of the Virginia Department of Historic Resources Accessed 29-Oct-2008.
- ↑ Bluemont Historic District marker in HMdb.org: The Historical Marker Database Accessed 29-Oct-2008.
- ↑ National Park Service (2010-07-09). "National Register Information System". National Register of Historic Places. National Park Service.
- ↑ http://www.purcellvillegazette.com/
- ↑ Climate Summary for Bluemont, Virginia