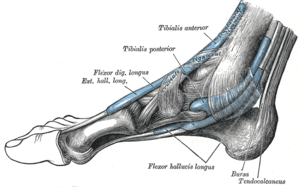
The flexor digitorum longus is situated on the tibial side of the leg. At its origin it is thin and pointed, but it gradually increases in size as it descends. This muscle serves to curl the second, third, fourth, and fifth toes (flexion of phalanges dscII-V).
Structure
It arises from the posterior surface of the body of the tibia, from immediately below the soleal line to within 7 or 8 cm. of its lower extremity, medial to the tibial origin of the Tibialis posterior; it also arises from the fascia covering the Tibialis posterior.
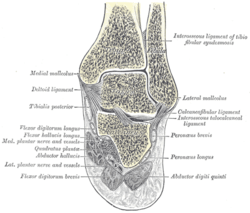
The fibers end in a tendon, which runs nearly the whole length of the posterior surface of the muscle. This tendon passes behind the medial malleolus, in a groove, common to it and the tibialis posterior, but separated from the latter by a fibrous septum, each tendon being contained in a special compartment lined by a separate mucous sheath. The tendon of the tibialis posterior and the tendon of the flexor digitorum longus cross each other, in a spot above the medial malleolus, the crural tendinous chiasm.[1][2][3]
It passes obliquely forward and lateralward, superficial to the deltoid ligament of the ankle-joint, into the sole of the foot, where it crosses below the tendon of the flexor hallucis longus (plantar tendinous chiasm),[1][2][3] and receives from it a strong tendinous slip.
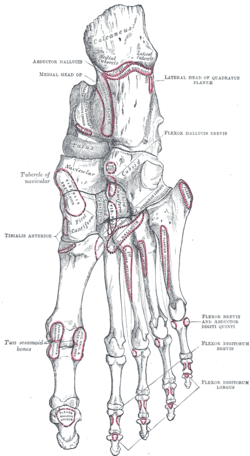
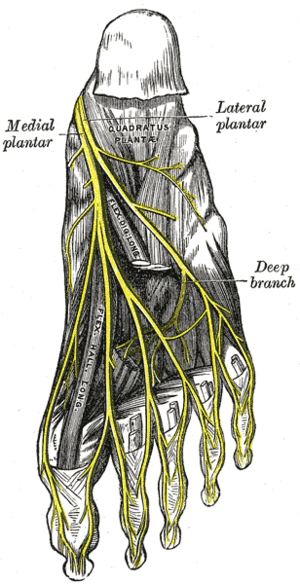
It then expands and is joined by the quadratus plantæ, and finally divides into four tendons, which are inserted into the bases of the last phalanges of the second, third, fourth, and fifth toes, each tendon passing through an opening in the corresponding tendon of the flexor digitorum brevis opposite the base of the first phalanx.
Variation
Flexor accessorius longus digitorum, not infrequent, origin from fibula, or tibia, or the deep fascia and ending in a tendon which, after passing beneath the laciniate ligament, joins the tendon of the long flexor or the quadratus plantæ.
Function
Similar to the flexor hallucis longus and tibialis posterior muscles, the flexor digitorum longus muscle functions to plantar flex and invert the foot. The flexor digitorum longus muscle is responsible for the movement and curling of the second, third, fourth and fifth toes. This muscle makes it possible for the toes to grip the surface of floors, which is important when it comes to maintaining postural balance on surfaces that are rough or uneven. The other deep muscles are the flexor digitorum longus and tibialis posterior; the tibialis posterior is the most powerful of these deep muscles. All three muscles are innervated by the tibial nerve which comprises half of the sciatic nerve.
Injury
After passing through the tarsal tunnel, the flexor digitorum longus tendon must curve around a bony landmark called the sustenaculum tali. Flexor digitorum longus pain can occur with a trip and fall on uneven surface when the toes are not able to grip the surface totally. One can also injure the flexor digitorum longus muscle while running on a beach in the sand without any footwear making the muscle vulnerable at the calcaneus attachment for injuries. In case of flexor digitorum longus pain or strain, the patient will find it tough to walk and will have excruciating pain in the feet and ankles. Support braces along with warm compresses are the most preferred way of treating flexor digitorum longus pain or strain.
Additional images
| Bones of the right leg. Posterior surface. |
| Bones of the right foot. Plantar surface. |
| Coronal section through right talocrural and talocalcaneal joints. |
| Muscles of the back of the leg. Deep layer. |
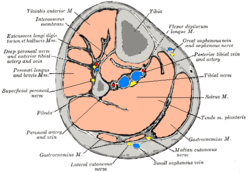
| Cross-section through middle of leg. |
| Muscles of the sole of the foot. Second layer. |
| Circumpatellar anastomosis. |
| Nerves of the right lower extremity Posterior view. |
| Muscles of the back of the leg. Deep layer. |
| Muscles of the back of the leg. Deep layer. |
| Muscles of the leg.Posterior view |
| Muscles of the sole of the foot |
| Dorsum and sole of Foot. Ankle joint. Deep dissection |
|
References
This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links