Gettysburg Address

| ||
|---|---|---|
|
President of the United States First term Second term Assassination and legacy
|
||
The Gettysburg Address is a speech by U.S. President Abraham Lincoln, one of the best-known in American history.[4][5] It was delivered by Lincoln during the American Civil War, on the afternoon of Thursday, November 19, 1863, at the dedication of the Soldiers' National Cemetery in Gettysburg, Pennsylvania, four and a half months after the Union armies defeated those of the Confederacy at the Battle of Gettysburg.
Abraham Lincoln's carefully crafted address, secondary to other presentations that day, was one of the greatest and most influential statements of national purpose. In just over two minutes, Lincoln reiterated the principles of human equality espoused by the Declaration of Independence[6] and proclaimed the Civil War as a struggle for the preservation of the Union sundered by the secession crisis,[7] with "a new birth of freedom"[8] that would bring true equality to all of its citizens.[9] Lincoln also redefined the Civil War as a struggle not just for the Union, but also for the principle of human equality.[6]
Beginning with the now-iconic phrase "Four score and seven years ago"—referring to the United States Declaration of Independence in 1776—Lincoln examined the founding principles of the United States as stated in the Declaration of Independence. In the context of the Civil War, Lincoln also memorialized the sacrifices of those who gave their lives at Gettysburg and extolled virtues for the listeners (and the nation) to ensure the survival of America's representative democracy: that "government of the people, by the people, for the people, shall not perish from the earth."
Despite the speech's prominent place in the history and popular culture of the United States, the exact wording and location of the speech are disputed. The five known manuscripts of the Gettysburg Address in Lincoln's hand differ in a number of details, and also differ from contemporary newspaper reprints of the speech. Modern scholarship locates the speakers' platform 40 yards (or more) away from the Traditional Site within Soldiers' National Cemetery at the Soldiers' National Monument and entirely within private, adjacent Evergreen Cemetery.

Background

Following the Battle of Gettysburg on July 1–3, 1863, reburial of Union soldiers from the Gettysburg Battlefield graves began on October 17. David Wills, of the committee for the November 19 Consecration of the National Cemetery at Gettysburg, invited President Lincoln: "It is the desire that, after the Oration, you, as Chief Executive of the nation, formally set apart these grounds to their sacred use by a few appropriate remarks."[10] Lincoln's address followed the oration by Edward Everett, who subsequently included a copy of the Gettysburg Address in his 1864 book about the event (Address of the Hon. Edward Everett At the Consecration of the National Cemetery At Gettysburg, 19th November 1863, with the Dedicatory Speech of President Lincoln, and the Other Exercises of the Occasion; Accompanied by An Account of the Origin of the Undertaking and of the Arrangement of the Cemetery Grounds, and by a Map of the Battle-field and a Plan of the Cemetery).
During the train trip from Washington, D.C., to Gettysburg on November 18, Lincoln remarked to John Hay that he felt weak. On the morning of November 19, Lincoln mentioned to John Nicolay that he was dizzy. In the railroad car the President rode with his secretary, John G. Nicolay, his assistant secretary, John Hay, the three members of his Cabinet who accompanied him, William Seward, John Usher and Montgomery Blair, several foreign officials and others. Hay noted that during the speech Lincoln's face had 'a ghastly color' and that he was 'sad, mournful, almost haggard.' After the speech, when Lincoln boarded the 6:30 pm train for Washington, D.C., he was feverish and weak, with a severe headache. A protracted illness followed, which included a vesicular rash and was diagnosed as a mild case of smallpox. It thus seems highly likely that Lincoln was in the prodromal period of smallpox when he delivered the Gettysburg address.[11]
Program and Everett's "Gettysburg Oration"
| Wikisource has original text related to this article: |

The program organized for that day by Wills and his committee included:
Music, by Birgfeld's Band[12] ("Homage d'uns Heros" by Adolph Birgfeld)Prayer, by Reverend T. H. Stockton, D.D.
Benediction, by Reverend H. L. Baugher, D.D.[10]
Music, by the Marine Band ("Old Hundred"), directed by Francis Scala
Oration, by Hon. Edward Everett ("The Battles of Gettysburg")
Music, Hymn ("Consecration Chant") by B. B. French, Esq., music by Wilson G Horner, sung by Baltimore Glee Club
Dedicatory Remarks, by the President of the United States
Dirge ("Oh! It is Great for Our Country to Die", words by James G. Percival, music by Alfred Delaney), sung by Choir selected for the occasion
While it is Lincoln's short speech that has gone down in history as one of the finest examples of English public oratory, it was Everett's two-hour oration that was slated to be the "Gettysburg address" that day. His now seldom-read 13,607-word oration began:
Standing beneath this serene sky, overlooking these broad fields now reposing from the labors of the waning year, the mighty Alleghenies dimly towering before us, the graves of our brethren beneath our feet, it is with hesitation that I raise my poor voice to break the eloquent silence of God and Nature. But the duty to which you have called me must be performed;—grant me, I pray you, your indulgence and your sympathy.[13]
And ended two hours later with:
But they, I am sure, will join us in saying, as we bid farewell to the dust of these martyr-heroes, that wheresoever throughout the civilized world the accounts of this great warfare are read, and down to the latest period of recorded time, in the glorious annals of our common country, there will be no brighter page than that which relates the Battles of Gettysburg.[14]
Lengthy dedication addresses like Everett's were common at cemeteries in this era. The tradition began in 1831 when Justice Joseph Story delivered the dedication address at Mount Auburn Cemetery in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Those addresses often linked cemeteries to the mission of Union.[15]
Text of Gettysburg Address
Shortly after Everett's well-received remarks, Lincoln spoke for only a few minutes.[16] With a "few appropriate remarks", he was able to summarize his view of the war in just ten sentences.
Despite the historical significance of Lincoln's speech, modern scholars disagree as to its exact wording, and contemporary transcriptions published in newspaper accounts of the event and even handwritten copies by Lincoln himself differ in their wording, punctuation, and structure.[17][18] Of these versions, the Bliss version, written well after the speech as a favor for a friend, is viewed by many as the standard text.[19] Its text differs, however, from the written versions prepared by Lincoln before and after his speech. It is the only version to which Lincoln affixed his signature, and the last he is known to have written.[19]
 |
Gettysburg Address
A modern recording of Lincoln's Gettysburg Address. |
| Problems playing this file? See media help. | |
Four score and seven years ago our fathers brought forth on this continent a new nation, conceived in liberty, and dedicated to the proposition that all men are created equal.Now we are engaged in a great civil war, testing whether that nation, or any nation so conceived and so dedicated, can long endure. We are met on a great battlefield of that war. We have come to dedicate a portion of that field, as a final resting place for those who here gave their lives that that nation might live. It is altogether fitting and proper that we should do this.
But, in a larger sense, we can not dedicate, we can not consecrate, we can not hallow this ground. The brave men, living and dead, who struggled here, have consecrated it, far above our poor power to add or detract. The world will little note, nor long remember what we say here, but it can never forget what they did here. It is for us the living, rather, to be dedicated here to the unfinished work which they who fought here have thus far so nobly advanced. It is rather for us to be here dedicated to the great task remaining before us—that from these honored dead we take increased devotion to that cause for which they gave the last full measure of devotion—that we here highly resolve that these dead shall not have died in vain—that this nation, under God, shall have a new birth of freedom—and that government of the people, by the people, for the people, shall not perish from the earth.
Lincoln's sources
In Lincoln at Gettysburg, Garry Wills notes the parallels between Lincoln's speech and Pericles's Funeral Oration during the Peloponnesian War as described by Thucydides. (James McPherson notes this connection in his review of Wills's book.[20] Gore Vidal also draws attention to this link in a BBC documentary about oration.[21]) Pericles' speech, like Lincoln's:
- Begins with an acknowledgment of revered predecessors: "I shall begin with our ancestors: it is both just and proper that they should have the honor of the first mention on an occasion like the present"
- Praises the uniqueness of the State's commitment to democracy: "If we look to the laws, they afford equal justice to all in their private differences"
- Honors the sacrifice of the slain, "Thus choosing to die resisting, rather than to live submitting, they fled only from dishonor, but met danger face to face"
- Exhorts the living to continue the struggle: "You, their survivors, must determine to have as unfaltering a resolution in the field, though you may pray that it may have a happier issue."[20][22]
In contrast, writer Adam Gopnik, in The New Yorker, notes that while Everett's Oration was explicitly neoclassical, referring directly to Marathon and Pericles, "Lincoln's rhetoric is, instead, deliberately Biblical. (It is difficult to find a single obviously classical reference in any of his speeches.) Lincoln had mastered the sound of the King James Bible so completely that he could recast abstract issues of constitutional law in Biblical terms, making the proposition that Texas and New Hampshire should be forever bound by a single post office sound like something right out of Genesis."[17]

Several theories have been advanced by Lincoln scholars to explain the provenance of Lincoln's famous phrase "government of the people, by the people, for the people".
The Prologue to John Wycliffe's first English translation of the Bible, which first appeared in 1384,[23] includes the phrase:
This Bible is for the government of the people, for the people and by the people.
In a discussion "A more probable origin of a famous Lincoln phrase",[24] in The American Monthly Review of Reviews, Albert Shaw credits a correspondent with pointing out the writings of William Herndon, Lincoln's law partner, who wrote in the 1888 work Abraham Lincoln: The True Story of A Great Life that he had brought to Lincoln some of the sermons of abolitionist minister Theodore Parker, of Massachusetts, and that Lincoln was moved by Parker's use of this idea:
I brought with me additional sermons and lectures of Theodore Parker, who was warm in his commendation of Lincoln. One of these was a lecture on 'The Effect of Slavery on the American People' ... which I gave to Lincoln, who read and returned it. He liked especially the following expression, which he marked with a pencil, and which he in substance afterwards used in his Gettysburg Address: 'Democracy is direct self-government, over all the people, for all the people, by all the people.'[25]
Craig R. Smith, in "Criticism of Political Rhetoric and Disciplinary Integrity", suggested Lincoln's view of the government as expressed in the Gettysburg Address was influenced by the noted speech of Massachusetts Senator Daniel Webster, the "Second Reply to Hayne", in which Webster famously thundered "Liberty and Union, now and forever, one and inseparable!"[26] Specifically, in this speech on January 26, 1830, before the United States Senate, Webster described the federal government as: "made for the people, made by the people, and answerable to the people", foreshadowing Lincoln's "government of the people, by the people, for the people".[27] Webster also noted, "This government, Sir, is the independent offspring of the popular will. It is not the creature of State legislatures; nay, more, if the whole truth must be told, the people brought it into existence, established it, and have hitherto supported it, for the very purpose, amongst others, of imposing certain salutary restraints on State sovereignties."[27]
A source predating these others with which Lincoln was certainly familiar was Chief Justice John Marshall's opinion in McCulloch v. Maryland (1819), a case asserting federal authority to create a national bank and to be free from the State's powers to tax. In asserting the superiority of federal power over the states, Chief Justice Marshall stated: "The government of the Union, then (whatever may be the influence of this fact on the case), is, emphatically and truly, a government of the people. In form, and in substance, it emanates from them. Its powers are granted by them, and are to be exercised directly on them, and for their benefit." Lincoln, a lawyer and President engaged in the greatest struggle of federalism, was (more eloquently) echoing the preeminent case that had solidified federal power over the States.
Wills observed Lincoln's usage of the imagery of birth, life, and death in reference to a nation "brought forth", "conceived", and that shall not "perish".[28] Others, including Allen C. Guelzo, the director of Civil War Era studies at Gettysburg College in Pennsylvania,[29] suggested that Lincoln's formulation "four score and seven" was an allusion to the King James Version of the Bible's Psalms 90:10, in which man's lifespan is given as "threescore years and ten; and if by reason of strength they be fourscore years".[30][31]
Five manuscripts
| Wikisource has original text related to this article: |
Each of the five known manuscript copies of the Gettysburg Address is named for the person who received it from Lincoln. Lincoln gave copies to his private secretaries, John Nicolay and John Hay.[32] Both of these drafts were written around the time of his November 19 address, while the other three copies of the address, the Everett, Bancroft, and Bliss copies, were written by Lincoln for charitable purposes well after November 19.[33][34] In part because Lincoln provided a title and signed and dated the Bliss copy, it has become the standard text of Lincoln's Gettysburg Address.[35]
Nicolay and Hay were appointed custodians of Lincoln's papers by Lincoln's son Robert Todd Lincoln in 1874.[32] After appearing in facsimile in an article written by John Nicolay in 1894, the Nicolay copy was presumably among the papers passed to Hay by Nicolay's daughter Helen upon Nicolay's death in 1901. Robert Lincoln began a search for the original copy in 1908, which resulted in the discovery of a handwritten copy of the Gettysburg Address among the bound papers of John Hay—a copy now known as the "Hay copy" or "Hay draft".[32]
The Hay draft differed from the version of the Gettysburg Address published by John Nicolay in 1894 in a number of significant ways: it was written on a different type of paper, had a different number of words per line and number of lines, and contained editorial revisions in Lincoln's hand.[32]
Both the Hay and Nicolay copies of the Address are within the Library of Congress, encased in specially designed, temperature-controlled, sealed containers with argon gas in order to protect the documents from oxidation and continued deterioration.[36]
Nicolay copy
The Nicolay copy[a] is often called the "first draft" because it is believed to be the earliest copy that exists.[37][38] Scholars disagree over whether the Nicolay copy was actually the reading copy Lincoln held at Gettysburg on November 19. In an 1894 article that included a facsimile of this copy, Nicolay, who had become the custodian of Lincoln's papers, wrote that Lincoln had brought to Gettysburg the first part of the speech written in ink on Executive Mansion stationery, and that he had written the second page in pencil on lined paper before the dedication on November 19.[37] Matching folds are still evident on the two pages, suggesting it could be the copy that eyewitnesses say Lincoln took from his coat pocket and read at the ceremony.[38][39] Others believe that the delivery text has been lost, because some of the words and phrases of the Nicolay copy do not match contemporary transcriptions of Lincoln's original speech.[40] The words "under God", for example, are missing in this copy from the phrase "that this nation shall have a new birth of freedom ..." In order for the Nicolay draft to have been the reading copy, either the contemporary transcriptions were inaccurate, or Lincoln would have had to depart from his written text in several instances. This copy of the Gettysburg Address apparently remained in John Nicolay's possession until his death in 1901, when it passed to his friend and colleague John Hay.[32] It used to be on display as part of the American Treasures exhibition of the Library of Congress in Washington, D.C.[41]
Hay copy

The existence of the Hay copy[b] was first announced to the public in 1906, after the search for the "original manuscript" of the Address among the papers of John Hay brought it to light.[32] Significantly, it differs somewhat from the manuscript of the Address described by John Nicolay in his article, and contains numerous omissions and inserts in Lincoln's own hand, including omissions critical to the basic meaning of the sentence, not simply words that would be added by Lincoln to strengthen or clarify their meaning. In this copy, as in the Nicolay copy, the words "under God" are not present.
This version has been described as "the most inexplicable" of the drafts and is sometimes referred to as the "second draft".[38][42] The "Hay copy" was made either on the morning of the delivery of the Address, or shortly after Lincoln's return to Washington. Those who believe that it was completed on the morning of his address point to the fact that it contains certain phrases that are not in the first draft but are in the reports of the address as delivered and in subsequent copies made by Lincoln. It is probable, they conclude, that, as stated in the explanatory note accompanying the original copies of the first and second drafts in the Library of Congress, Lincoln held this second draft when he delivered the address.[43] Lincoln eventually gave this copy to his other personal secretary, John Hay, whose descendants donated both it and the Nicolay copy to the Library of Congress in 1916.[44]
Everett copy
The Everett copy,[c] also known as the "Everett-Keyes copy", was sent by President Lincoln to Edward Everett in early 1864, at Everett's request. Everett was collecting the speeches at the Gettysburg dedication into one bound volume to sell for the benefit of stricken soldiers at New York's Sanitary Commission Fair. The draft Lincoln sent became the third autograph copy, and is now in the possession of the Illinois State Historical Library in Springfield, Illinois,[43] where it is currently on display in the Treasures Gallery of the Abraham Lincoln Presidential Library and Museum.
Bancroft copy
The Bancroft copy[d] of the Gettysburg Address was written out by President Lincoln in February 1864 at the request of George Bancroft, the famed historian and former Secretary of the Navy, whose comprehensive ten-volume History of the United States later led him to be known as the "father of American History".[45][46] Bancroft planned to include this copy in Autograph Leaves of Our Country's Authors, which he planned to sell at a Soldiers' and Sailors' Sanitary Fair in Baltimore. As this fourth copy was written on both sides of the paper, it proved unusable for this purpose, and Bancroft was allowed to keep it. This manuscript is the only one accompanied both by a letter from Lincoln transmitting the manuscript and by the original envelope addressed and franked by Lincoln.[47] This copy remained in the Bancroft family for many years, was sold to various dealers and purchased by Nicholas and Marguerite Lilly Noyes,[48] who donated the manuscript to Cornell in 1949. It is now held by the Division of Rare and Manuscript Collections in the Carl A. Kroch Library at Cornell University.[43] It is the only one of the five copies to be privately owned.[49]
Bliss copy

Discovering that his fourth written copy could not be used, Lincoln then wrote a fifth draft, which was accepted for the purpose requested. The Bliss copy,[e] named for Colonel Alexander Bliss, Bancroft's stepson and publisher of Autograph Leaves, is the only draft to which Lincoln affixed his signature. Lincoln is not known to have made any further copies of the Gettysburg Address. Because of the apparent care in its preparation, and in part because Lincoln provided a title and signed and dated this copy, it has become the standard version of the address and the source for most facsimile reproductions of Lincoln's Gettysburg Address. It is the version that is inscribed on the South wall of the Lincoln Memorial.[35]
This draft is now displayed in the Lincoln Room of the White House, a gift of Oscar B. Cintas, former Cuban Ambassador to the United States.[43] Cintas, a wealthy collector of art and manuscripts, purchased the Bliss copy at a public auction in 1949 for $54,000 ($538,000 as of 2016), at that time the highest price ever paid for a document at public auction.[50] Cintas' properties were claimed by the Castro government after the Cuban Revolution in 1959, but Cintas, who died in 1957, willed the Gettysburg Address to the American people, provided it would be kept at the White House, where it was transferred in 1959.[51]
Garry Wills concluded the Bliss copy "is stylistically preferable to others in one significant way: Lincoln removed 'here' from 'that cause for which they (here) gave ...' The seventh 'here' is in all other versions of the speech." Wills noted the fact that Lincoln "was still making such improvements", suggesting Lincoln was more concerned with a perfected text than with an 'original' one.[52]
From November 21, 2008, to January 1, 2009, the Albert H. Small Documents Gallery at the Smithsonian Institution National Museum of American History hosted a limited public viewing of the Bliss copy, with the support of then-First Lady Laura Bush. The Museum also launched an online exhibition and interactive gallery to enable visitors to look more closely at the document.[53]
Others
Another contemporary source of the text is the Associated Press dispatch, transcribed from the shorthand notes taken by reporter Joseph L. Gilbert. It also differs from the drafted text in a number of minor ways.[54][55]
Contemporary sources and reaction

Eyewitness reports vary as to their view of Lincoln's performance. In 1931, the printed recollections of 87-year-old Mrs. Sarah A. Cooke Myers, who was 19 when she attended the ceremony, suggest a dignified silence followed Lincoln's speech: "I was close to the President and heard all of the Address, but it seemed short. Then there was an impressive silence like our Menallen Friends Meeting. There was no applause when he stopped speaking."[57] According to historian Shelby Foote, after Lincoln's presentation, the applause was delayed, scattered, and "barely polite".[58] In contrast, Pennsylvania Governor Curtin maintained, "He pronounced that speech in a voice that all the multitude heard. The crowd was hushed into silence because the President stood before them ... It was so Impressive! It was the common remark of everybody. Such a speech, as they said it was!"[59] Reinterment of soldiers' remains from field graves into the cemetery, which had begun within months of the battle, was less than half complete on the day of the ceremony.[60]
In an oft-repeated legend, Lincoln is said to have turned to his bodyguard Ward Hill Lamon and remarked that his speech, like a bad plow, "won't scour". According to Garry Wills, this statement has no basis in fact and largely originates from the unreliable recollections of Lamon.[10] In Garry Wills's view, "[Lincoln] had done what he wanted to do [at Gettysburg]".
In a letter to Lincoln written the following day, Everett praised the President for his eloquent and concise speech, saying, "I should be glad if I could flatter myself that I came as near to the central idea of the occasion, in two hours, as you did in two minutes."[61] Lincoln replied that he was glad to know the speech was not a "total failure".[61]
Other public reaction to the speech was divided along partisan lines.[6] The Democratic-leaning Chicago Times observed, "The cheek of every American must tingle with shame as he reads the silly, flat and dishwatery utterances of the man who has to be pointed out to intelligent foreigners as the President of the United States."[62] In contrast, the Republican-leaning New York Times was complimentary and printed the speech.[56] In Massachusetts, the Springfield Republican also printed the entire speech, calling it "a perfect gem" that was "deep in feeling, compact in thought and expression, and tasteful and elegant in every word and comma". The Republican predicted that Lincoln's brief remarks would "repay further study as the model speech".[63] On the sesquicentennial of the address, The Patriot-News of Harrisburg, Pennsylvania, formerly the Patriot & Union, retracted its original reaction ("silly remarks" deserving "the veil of oblivion") stating: "Seven score and ten years ago, the forefathers of this media institution brought forth to its audience a judgment so flawed, so tainted by hubris, so lacking in the perspective history would bring, that it cannot remain unaddressed in our archives. ... the Patriot & Union failed to recognize [the speech's] momentous importance, timeless eloquence, and lasting significance. The Patriot-News regrets the error."[64][65]
Foreign newspapers also criticized Lincoln's remarks. The Times of London commented: "The ceremony [at Gettysburg] was rendered ludicrous by some of the luckless sallies of that poor President Lincoln."[66]
Congressman Joseph A. Goulden, then an eighteen-year-old school teacher, was present and heard the speech. He served in the United States Marine Corps during the war, and later had a successful career in insurance in Pennsylvania and New York City before entering Congress as a Democrat. In his later life, Goulden was often asked about the speech, since the passage of time made him one of a dwindling number of individuals who had been present for it. He commented on the event and Lincoln's speech in favorable terms, naming Lincoln's address as one of the inspirations for him to enter military service. Goulden's recollections included remarks to the House of Representatives in 1914.[67][68]
Audio recollections
William R. Rathvon is the only known eyewitness of both Lincoln's arrival at Gettysburg and the address itself to have left an audio recording of his recollections.[69] One year before his death in 1939, Rathvon's reminiscences were recorded on February 12, 1938, at the Boston studios of radio station WRUL, including his reading the address, itself, and a 78 rpm record was pressed. The title of the 78 record was "I Heard Lincoln That Day – William R. Rathvon, TR Productions". A copy wound up at National Public Radio (NPR) during a "Quest for Sound" project in 1999.[70] NPR continues to air it around Lincoln's birthday.
Like most people who came to Gettysburg, the Rathvon family was aware that Lincoln was going to make some remarks. The family went to the town square where the procession was to form to go out to the cemetery that had not been completed yet. At the head of the procession rode Lincoln on a gray horse preceded by a military band that was the first the young boy had ever seen. Rathvon describes Lincoln as so tall and with such long legs that they went almost to the ground; he also mentions the long eloquent speech given by Edward Everett of Massachusetts whom Rathvon accurately described as the "most finished orator of the day". Rathvon then goes on to describe how Lincoln stepped forward and "with a manner serious almost to sadness, gave his brief address".[71] During the delivery, along with some other boys, young Rathvon wiggled his way forward through the crowd until he stood within 15 feet of Mr. Lincoln and looked up into what he described as Lincoln's "serious face". Rathvon recalls candidly that, although he listened "intently to every word the president uttered and heard it clearly", he explains, "boylike, I could not recall any of it afterwards". But he explains that if anyone said anything disparaging about "honest Abe", there would have been a "junior battle of Gettysburg". In the recording Rathvon speaks of Lincoln's speech allegorically "echoing through the hills".
Photographs

The only known and confirmed photograph of Lincoln at Gettysburg,[72] taken by photographer David Bachrach[73] was identified in the Mathew Brady collection of photographic plates in the National Archives and Records Administration in 1952. While Lincoln's speech was short and may have precluded multiple pictures of him while speaking, he and the other dignitaries sat for hours during the rest of the program. Given the length of Everett's speech and the length of time it took for 19th-century photographers to get "set up" before taking a picture, it is quite plausible that the photographers were ill-prepared for the brevity of Lincoln's remarks.
Usage of "under God"
The words "under God" do not appear in the Nicolay and Hay drafts but are included in the three later copies (Everett, Bancroft, and Bliss). Accordingly, some skeptics maintain that Lincoln did not utter the words "under God" at Gettysburg.[74][75] However, at least three reporters telegraphed the text of Lincoln's speech on the day the Address was given with the words "under God" included. Historian William E. Barton argues that:[76]
Every stenographic report, good, bad and indifferent, says 'that the nation shall, under God, have a new birth of freedom.' There was no common source from which all the reporters could have obtained those words but from Lincoln's own lips at the time of delivery. It will not do to say that [Secretary of War] Stanton suggested those words after Lincoln's return to Washington, for the words were telegraphed by at least three reporters on the afternoon of the delivery.
The reporters present included Joseph Gilbert, from the Associated Press; Charles Hale, from the Boston Advertiser;[77] John R. Young (who later became the Librarian of Congress), from the Philadelphia Press; and reporters from the Cincinnati Commercial,[78] New York Tribune,[79] and The New York Times.[79] Charles Hale "had notebook and pencil in hand, [and] took down the slow-spoken words of the President".[80] "He took down what he declared was the exact language of Lincoln's address, and his declaration was as good as the oath of a court stenographer. His associates confirmed his testimony, which was received, as it deserved to be, at its face value."[81] One explanation is that Lincoln deviated from his prepared text and inserted the phrase when he spoke. Ronald C. White, visiting professor of history at the University of California – Los Angeles and professor of American religious history emeritus at the San Francisco Theological Seminary, wrote in this context of Lincoln's insertion and usage of "under God":
It was an uncharacteristically spontaneous revision for a speaker who did not trust extemporaneous speech. Lincoln had added impromptu words in several earlier speeches, but always offered a subsequent apology for the change. In this instance, he did not. And Lincoln included "under God" in all three copies of the address he prepared at later dates. "Under God" pointed backward and forward: back to "this nation", which drew its breath from both political and religious sources, but also forward to a "new birth". Lincoln had come to see the Civil War as a ritual of purification. The old Union had to die. The old man had to die. Death became a transition to a new Union and a new humanity.[8]
The phrase "under God" was used frequently in works published before 1860, usually with the meaning "with God's help".[82]
Platform location
Outside the Cemetery and within sight of the cross-walk, a historical marker proclaims:
Nearby, Nov. 19, 1863, in dedicating the National Cemetery, Abraham Lincoln gave the address which he had written in Washington and revised after his arrival at Gettysburg the evening of November 18.[84]
Directly inside the Taneytown Road entrance are located the Rostrum and the Lincoln Address Memorial. Neither of these is located within 300 yards of any of the five (or more) claimed locations for the dedicatory platform.[85]
Pre-modern

Colonel W. Yates Selleck was a marshal in the parade on Consecration Day and was seated on the platform when Lincoln made the address.[86] Selleck marked a map with the position of the platform and described it as "350 feet almost due north of Soldiers' National Monument, 40 feet from a point in the outer circle of lots where [the] Michigan and New York [burial sections] are separated by a path".[87] A location which approximates this description is 39°49.243′N, 77°13.869′W.
As pointed out in 1973 by retired park historian Frederick Tilberg, the Selleck Site is 25 feet lower than the crest of Cemetery Hill, and only the crest presents a panoramic view of the battlefield. A spectacular view from the location of the speech was noted by many eyewitnesses, is consistent with the Traditional Site at the Soldiers' National Monument (and other sites on the crest) but is inconsistent with the Selleck Site.[88][89]
The Kentucky Memorial was erected in 1975, is located directly adjacent to the Soldiers' National Monument, and states, "Kentucky honors her son, Abraham Lincoln, who delivered his immortal address at the site now marked by the soldiers' monument."[90] With its position at the center of the concentric rings of soldiers' graves and the continuing endorsement of Lincoln's native state the Soldiers' National Monument persists as a credible location for the speech.
Writing a physical description of the layout for the Gettysburg National Cemetery under construction in November 1863, the correspondent from the Cincinnati Daily Commercial described the dividing lines between the state grave plots as "the radii of a common center, where a flag pole is now raised, but where it is proposed to erect a national monument".[91] With the inclusion of this quotation Tilberg inadvertently verifies a central principle of future photographic analyses—a flagpole, rather than the speakers' platform, occupied the central point of the soldiers' graves. In fact, the precision of the photo-analyses relies upon the coincidence of position between this temporary flag pole and the future monument.
Confusing to today's tourist, the Kentucky Memorial is contradicted by a newer marker which was erected nearby by the Gettysburg National Military Park and locates the speakers' platform inside Evergreen Cemetery.[92] Similarly, outdated National Park Service documents which pinpoint the location at the Soldiers' National Monument have not been systematically revised since the placement of the newer marker.[93][94] Miscellaneous web pages perpetuate the Traditional Site.[95][96][97]
Photo analysis
2-D and optical stereoscopy
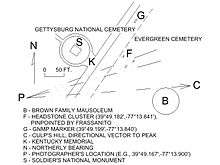
Based upon photographic analysis, the Gettysburg National Military Park (G.N.M.P.) placed a marker (near 39°49.199′N 77°13.840′W / 39.819983°N 77.230667°W) which states, "The speakers' platform was located in Evergreen Cemetery to your left."[98][99] The observer of this marker stands facing the fence which separates the two cemeteries (one public and one private).
In 1982, Senior Park Historian Kathleen Georg Harrison first analyzed photographs and proposed a location in Evergreen Cemetery but has not published her analysis. Speaking for Harrison without revealing details, two sources characterize her proposed location as "on or near [the] Brown family vault" in Evergreen Cemetery.[100][101]
William A. Frassanito, a former military intelligence analyst, documented a comprehensive photographic analysis in 1995, and it associates the location of the platform with the position of specific modern headstones in Evergreen Cemetery. According to Frassanito, the extant graves of Israel Yount (died 1892)(39°49.180′N 77°13.845′W / 39.819667°N 77.230750°W), John Koch (died 1913)(39°49.184′N 77°13.847′W / 39.819733°N 77.230783°W), and George E. Kitzmiller (died 1874)(39°49.182′N 77°13.841′W / 39.819700°N 77.230683°W) are among those which occupy the location of the 1863 speaker's stand.[102]
3-D photo-rendering and -animation
Assistant Professor of New Media at the University of North Carolina at Asheville, Christopher Oakley and his students are "working to produce a lifelike virtual 3-D re-creation of Lincoln delivering the Gettysburg Address" as part of the Virtual Lincoln Project. After taking precise measurements, some using lasers, and countless photographs on Cemetery Hill in 2013, Oakley's team used 3-D animation software Maya to estimate locations for the platform and the photographers who recorded its occupants. This work remains under development.[103]
Resolution

The GNMP marker, Wills' interpretation of Harrison's analysis, and the Frassanito analysis concur that the platform was located in private Evergreen Cemetery, rather than public Soldiers' National Cemetery. The National Park Service's National Cemetery Walking Tour brochure is one NPS document which agrees:
The Soldiers' National Monument, long misidentified as the spot from which Lincoln spoke, honors the fallen soldiers. [The location of the speech] was actually on the crown of this hill, a short distance on the other side of the iron fence and inside the Evergreen Cemetery, where President Lincoln delivered the Gettysburg Address to a crowd of some 15,000 people.[104]
While the GNMP marker is unspecific, providing only "to your left", the locations determined by the Harrison/Wills analysis and the Frassanito analysis differ by 40 yards. Frassanito has documented 1) his own conclusion, 2) his own methods and 3) a refutation of the Harrison site,[105] but neither the GNMP nor Harrison has provided any documentation. Each of the three points to a location in Evergreen Cemetery, as do modern NPS publications.
Although Lincoln dedicated the Gettysburg National Cemetery, the monument at the Cemetery's center actually has nothing to do with Lincoln or his famous speech. Intended to symbolize Columbia paying tribute to her fallen sons, its appreciation has been commandeered by the thirst for a tidy home for the speech.[106] Freeing the Cemetery and Monument to serve their original purpose, honoring of Union departed, is as unlikely as a resolution to the location controversy and the erection of a public monument to the speech in the exclusively private Evergreen Cemetery.[107]
Legacy
.jpg)
The importance of the Gettysburg Address in the history of the United States is underscored by its enduring presence in American culture. In addition to its prominent place carved into a stone cella on the south wall of the Lincoln Memorial in Washington, D.C., the Gettysburg Address is frequently referred to in works of popular culture, with the implicit expectation that contemporary audiences will be familiar with Lincoln's words.
In the many generations that have passed since the Address, it has remained among the most famous speeches in American history,[108] and is often taught in classes about history or civics.[109] Lincoln's Gettysburg Address is itself referenced in another of those famed orations, Martin Luther King, Jr.'s "I Have a Dream" speech.[110] Standing on the steps of the Lincoln Memorial in August 1963, King began with a reference, by the style of his opening phrase, to President Lincoln and his enduring words: "Five score years ago, a great American, in whose symbolic shadow we stand today, signed the Emancipation Proclamation. This momentous decree came as a great beacon light of hope to millions of Negro slaves who had been seared in the flames of withering injustice."
Phrases from the Address are often used or referenced in other works. The current Constitution of France states that the principle of the Republic of France is "gouvernement du peuple, par le peuple et pour le peuple" ("government of the people, by the people, and for the people"), a literal translation of Lincoln's words.[111] Sun Yat-Sen's "Three Principles of the People" were inspired from that phrase as well.[112] The aircraft carrier USS Abraham Lincoln has as its ship's motto the phrase "shall not perish".[113][114]
U.S. Senator Charles Sumner of Massachusetts wrote of the address and its enduring presence in American culture after Lincoln's assassination in April 1865: "That speech, uttered at the field of Gettysburg ... and now sanctified by the martyrdom of its author, is a monumental act. In the modesty of his nature he said 'the world will little note, nor long remember what we say here; but it can never forget what they did here.' He was mistaken. The world at once noted what he said, and will never cease to remember it."[6]
U.S. President John F. Kennedy stated in July 1963 about the battle and Lincoln's speech: "Five score years ago the ground on which we here stand shuddered under the clash of arms and was consecrated for all time by the blood of American manhood. Abraham Lincoln, in dedicating this great battlefield, has expressed, in words too eloquent for paraphrase or summary, why this sacrifice was necessary."[115] Sadly, Kennedy would meet the same fate as Abraham Lincoln only three days after the Gettysburg Address centennial.
In 2015, the Abraham Lincoln Presidential Library Foundation compiled Gettysburg Replies: The World Responds to Abraham Lincoln's Gettysburg Address. The work challenges leaders to craft 272 word responses to celebrate Abraham Lincoln, the Gettysburg Address, or a related topic.[116] One of the replies was by astrophysicist Neil deGrasse Tyson in which he made the point that one of Lincoln's greatest legacies was establishing, in the same year of the Gettysburg Address, the National Academy of Sciences, which had the longterm effect of "setting our Nation on a course of scientifically enlightened governance, without which we all may perish from this Earth".[117]
See also
Notes
- a The Gettysburg Address: Nicolay copy. The Library of Congress. Retrieved on 2010-09-15.
- b The Gettysburg Address: Hay copy. The Library of Congress. Retrieved on 2010-09-15.
- c Everett copy (jpg). virtualgettsyburg.com. Retrieved from internet archive 2007-06-14 version on 2007-12-10.
- d Bancroft copy cover letter (pic), Bancroft copy, page 1 (pic), page 2 (pic). Cornell University Library. Retrieved on 2007-12-11.
- e Bliss copy, page 1 (jpg), page 2 (jpg), page 3 (jpg). Illinois Historic Preservation Agency. Retrieved on 2007-12-11.
References
- ↑ "Ultrarare photo of Abraham Lincoln discovered". Fox News. September 24, 2013. Retrieved September 25, 2013.
- ↑ Lidz, Franz (October 2013). "Will the Real Abraham Lincoln Please Stand Up?". Smithsonian. Retrieved October 3, 2013.
- ↑ Brian, Wolly (October 2013). "Interactive: Seeking Abraham Lincoln at the Gettysburg Address". Smithsonian. Retrieved October 3, 2013.
- ↑ Conant, Sean (2015). The Gettysburg Address: Perspectives on Lincoln's Greatest Speech. New York, NY: Oxford University Press. p. ix. ISBN 978-0-19-022745-6.
- ↑ Holsinger, M. Paul (1999). War and American Popular Culture: A Historical Encyclopedia. Westport, CT: Greenwood Press. p. 102. ISBN 978-0-313-29908-7.
- 1 2 3 4 "The Gettysburg Address". History. Retrieved February 22, 2013.
- ↑ Robert J. McNamara. "Emancipation Proclamation". www.about.com 19th Century History. Retrieved March 7, 2012.
- 1 2 White Jr., Ronald C. The Words That Moved a Nation in: "Abraham Lincoln A Legacy of Freedom", Washington, D.C.: U.S. Department of State – Bureau of International Information Programs, p. 58.
- ↑ Fox, Christopher Graham (September 12, 2008). "A analysis of Abraham Lincoln's poetic Gettysburg Address". foxthepoet.blogspot.de. Retrieved August 21, 2012.
- 1 2 3 Wills, Garry. Lincoln at Gettysburg. New York: Simon & Schuster, 1992, pp. 24–25, p. 35, pp. 34–35, p. 36.
- ↑ Goldman, A. S.; Schmalstieg Jr, F. C. (2007). "Abraham Lincoln's Gettysburg illness". Journal of medical biography. 15 (2): 104–10. doi:10.1258/j.jmb.2007.06-14. PMID 17551612.
- ↑ Boritt, Gabor. The Gettysburg Gospel: The Lincoln Speech That Nobody Knows. Simon & Schuster, 2008.
- ↑ Murphy, Jim (2000). Long Road to Gettysburg. Houghton Mifflin Company. p. 5. ISBN 978-0-618-05157-1. Retrieved December 10, 2007.
- ↑ Reid, Ronald F. (1990). Edward Everett: Unionist Orator. Volume 7. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 192. ISBN 978-0-313-26164-0. Retrieved December 10, 2007.
- ↑ Alfred L. Brophy, "'These Great and Beautiful Republics of the Dead': Public Constitutionalism and the Antebellum Cemetery"
- ↑ Murphy, Jim. The Long Road to Gettysburg, New York: Clarion Books, 1992. p. 105, "with a pronounced Kentucky accent".
- 1 2 Gopnik, Adam (May 28, 2007). "Angels and Ages: Lincoln's language and its legacy". Retrieved November 23, 2007. Gopnik notes, "Gabor Boritt, in his book The Gettysburg Gospel, has a thirty-page appendix that compares what Lincoln (probably) read at the memorial with what people heard and reported. Most of the differences are small, and due to understandable confusions ... A few disputes seem more significant."
- ↑ Also note Johnson's reference that "In 1895 Congress had voted to place at Gettysburg a bronze tablet engraved with the address but had mandated a text that does not correspond to any in Lincoln's hand or to contemporary newspaper accounts. The statute is reprinted in Henry Sweetser Burrage, Gettysburg and Lincoln: The Battle, the Cemetery, and the National Park (New York: G. P. Putnam's Sons, 1906), 211."
- 1 2 Boritt, Gabor. The Gettysburg Gospel: The Lincoln Speech That Nobody Knows., Appendix B p. 290: "This is the only copy that ... Lincoln dignified with a title: 'Address delivered at the dedication of the cemetery at Gettysburg.', a rare full signature, and the date: 'November 19, 1863.' ..This final draft, generally considered the standard text, remained in the Bliss family until 1949."
- 1 2 McPherson, James M (July 16, 1992). "The Art of Abraham Lincoln". The New York Review of Books. Archived from the original on July 11, 2011. Retrieved November 30, 2007.
- ↑ "Yes We Can! The Lost Art Of Oratory". BBC Two. April 5, 2009.
- ↑ "Pericles' Funeral Oration from Thucydides: Peloponnesian War". Liberty Library of Constitutional Classics. The Constitution Society. 2007. Retrieved November 30, 2007.
- ↑ Hannan, Dan. "150 years ago today, Abraham Lincoln praised 'government of the people, by the people, for the people' – but the words were not his". Retrieved November 19, 2013.
- ↑ Shaw, Albert, ed. The American Monthly Review of Reviews. Vol. XXIII, January–June 1901. New York: The Review of Reviews Company, 1901. p. 336.
- ↑ Herndon, William H. and Jesse W. Welk. Abraham Lincoln: The True Story of A Great Life New York: D. Appleton and Company, 1892. Vol II., p. 65.
- ↑ Smith, Craig (Fall 2000). "Criticism of Political Rhetoric and Disciplinary Integrity". American Communication Journal. 4 (1). Archived from the original on May 5, 2009. Retrieved November 26, 2007.
- 1 2 "The Second Reply to Hayne (January 26–27, 1830)". Daniel Webster: Dartmouth's Favorite Son. Dartmouth. Retrieved November 30, 2007. Webster himself may have been relying on earlier use of similar language. For example, John Hobhouse, 1st Baron Broughton had employed similar phraseology in 1819: "I am a man chosen for the people, by the people; and, if elected, I will do no other business than that of the people." See Broughton, John and Burdett, Francis. An Authentic Narrative of the Events of the Westminster Election, which Commenced on Saturday, February 13th, and Closed on Wednesday, March 3d, 1819 page 105 (Published by R. Stodart, 1819).
- ↑ Vosmeier, Matthew Noah (January–February 1992). "Lincoln and the 'Central Idea of the Occasion': Garry Wills's Lincoln at Gettysburg: The Words that Remade America.". Lincoln Lore. The Lincoln Museum. Retrieved November 9, 2009.
- ↑ Guelzo, Allen C (November 21, 2006). "When the Court lost its Conscience". The Wall Street Journal. Archived from the original on February 14, 2009. Retrieved November 26, 2006.
- ↑ McInerney, Daniel J (September 2000). "Review of Allen C. Guelzo, Abraham Lincoln: Redeemer President". H-Pol, H-Net Reviews. Retrieved November 30, 2007.
- ↑ Guelzo, Allen C (1999). Abraham Lincoln: Redeemer President. Grand Rapids, Michigan: William B. Eerdmans Publishing Co. ISBN 0-8028-3872-3.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Johnson, Martin P (Summer 2003). "Who Stole the Gettysburg Address". Journal of the Abraham Lincoln Association. 24 (2): 1–19.
- ↑ Rao, Maya (April 6, 2005). "C.U. Holds Gettysburg Address". Cornell Daily Sun. Retrieved November 23, 2007.: "Several months after President Abraham Lincoln delivered his Gettysburg address, renowned historian George Bancroft attended a reception at the White House. There, he asked Lincoln for a hand-written copy of the address, and that manuscript is now the highlight of Cornell University Library's Division of Rare and Manuscript Collections." "[Visitors] ... can also see the letter Lincoln enclosed when he mailed the copy to Bancroft, which is dated February 29, 1864."
- ↑ White, Ronald C. Jr. The Eloquent President: A Portrait of Lincoln Through His Words. New York: Random House, 2005. ISBN 1-4000-6119-9 Appendix 9, p. 390: "The Bliss copy ... Lincoln made in March 1864 ... The Everett and Bancroft copies, both of which Lincoln made in February 1864."
- 1 2 Boritt, Gabor (November 16, 2006). "In Lincoln's Hand". Wall Street Journal. Archived from the original on February 13, 2009. Retrieved November 23, 2007.
- ↑ "Preservation of the drafts of the Gettysburg Address at the Library of Congress". Library of Congress. Retrieved September 15, 2010.
- 1 2 Nicolay, J. "Lincoln's Gettysburg Address", Century Magazine 47 (February 1894): 596–608, cited by Johnson, Martin P. "Who Stole the Gettysburg Address", Journal of the Abraham Lincoln Association 24(2) (Summer 2003): 1–19.
- 1 2 3 "The Gettysburg Address Nicolay draft". Library of Congress. Retrieved September 15, 2010.
- ↑ Sandburg, Carl. "Lincoln Speaks at Gettysburg". In: Abraham Lincoln: The War Years (1939) New York: Harcourt, Brace & Company. II, 452–57; cited by Prochnow, Victor Herbert. ed. Great Stories from Great Lives Freeport: Books for Libraries Press, 1944. ISBN 0-8369-2018-X, p. 13: "The Cincinnati Commercial reporter wrote 'The President rises slowly, draws from his pocket a paper ... [and] reads the brief and pithy remarks."
- ↑ Wills, Garry. Appendix I: "this text does not have three important phrases that the joint newspaper accounts prove he actually spoke," and "there is no physical impossibility that this is the delivery text, but it is ... unlikely that it is."
- ↑ Top Treasures. American Treasures of the Library of Congress. Retrieved on 2007-12-10.
- ↑ David Mearns, "Unknown at this Address", in Lincoln and the Gettysburg Address: Commemorative Papers, ed. Allan Nevins (Urbana: University of Illinois Press, 1964), 133; Mearns and Dunlap, caption describing the facsimile of the Hay text in Long Remembered.; both cited in Johnson, "Who Stole the Gettysburg Address".
- 1 2 3 4 "Gettysburg National Military Park". United States Department of the Interior, National Park Service. Retrieved December 3, 2007. Historical Handbook Number Nine 1954 (Revised 1962), at the Gettysburg National Military Park Historical Handbook website.
- ↑ "The Gettysburg Address Hay draft". Library of Congress. September 15, 2010. Retrieved September 15, 2010.
- ↑ "George Bancroft". Encyclopædia Britannica Online. Retrieved December 19, 2007.
- ↑ See also: George Bancroft. Encarta. Archived from the original on October 31, 2009. Retrieved December 19, 2007.
- ↑ "Gettysburg Address". Cornell University Library. Retrieved December 19, 2007.
- ↑ "Founding Collections: Nicholas H. Noyes '06 and Marguerite Lilly Noyes". Cornell University Library. Retrieved November 28, 2007.
- ↑ "C.U. Holds Gettysburg Address Manuscript". The Cornell Daily Sun. April 6, 2005. Retrieved December 18, 2005.
- ↑ "About Cintas: Oscar B. Cintas". Oscar B. Cintas foundation. Retrieved December 10, 2007.
- ↑ Boritt, Gabor (November 16, 2006). "Change of Address: The Gettysburg drafts". The Wall Street Journal. p. D6. Retrieved December 4, 2006.
- ↑ Wills, Appendix I.
- ↑ "The Gettysburg Address". National Museum of American History, Smithsonian Institution. Retrieved April 4, 2012.
- ↑ Bryan, William Jennings, ed. 1906. The World's Famous Orations Vol. IX. America: II. (1818–1865). "V. The Speech at Gettysburg by Abraham Lincoln.". Retrieved December 18, 2005.
- ↑ "1846–1900: The News Cooperative Takes Shape". History/Archives: The Associated Press. Associated Press.org. Archived from the original on July 29, 2011. Retrieved November 30, 2007.
- 1 2 "The Heroes of July; A Solemn and Imposing Event. Dedication of the National Cemetery at Gettysburgh". The New York Times. November 20, 1863. p. 1. Archived from the original on June 9, 2009. Retrieved November 23, 2007. Full article in PDF available here .
- ↑ Hark, Ann. "Mrs. John T. Myers Relives the Day She Met the Great Emancipator". Recollections of Abraham Lincoln at Gettysburg. Abraham Lincoln online. Retrieved November 30, 2007. Citing the Philadelphia Public Ledger of February 7, 1932.
- ↑ Foote, Shelby (1986) [1958]. The Civil War, A Narrative: Fredericksburg to Meridian. Vintage Books. p. 832. ISBN 0-394-74621-X.
- ↑ "Abraham Lincoln at Gettysburg Cemetery". Lincoln at Gettysburg Photo Tour. Abraham Lincoln Online. 2007. Retrieved December 18, 2005.
- ↑ "Gettysburg Address Information". Dobbin House Inc. 1996–2006. Retrieved November 30, 2007. at gettysburg.com.
- 1 2 Simon, et al., eds. The Lincoln Forum: Abraham Lincoln, Gettysburg, and the Civil War. Mason City: Savas Publishing Company, 1999. ISBN 1-882810-37-6, p. 41.
- ↑ Sandburg, Carl Abraham Lincoln: The Prairie Years and the War Years, Harcourt, Brace & World, 1954, p. 445.
- ↑ Prochow, Herbert Victor, Great Stories from Great Lives. Harper & Brothers, 1944, p. 17.
- ↑ Patriot-News Editorial Board (November 14, 2013). "Retraction for our 1863 editorial calling Gettysburg Address 'silly remarks': Editorial". Patriot-News. Retrieved November 19, 2013.
- ↑ Stewart, Doug (November 18, 2013). "My Great-Great-Grandfather Hated the Gettysburg Address. 150 Years Later, He's Famous For It.". The Smithsonian's Past Imperfect (Blog). Retrieved November 19, 2013.
- ↑ "The Civil War In America". London: The Times. December 4, 1863. p. 9. Retrieved June 3, 2014. (subscription required (help)).
- ↑ United National Association of Post Office Clerks, The Post Office Clerk magazine, Volumes 13–14, January 1914, p. 6.
- ↑ United States House of Representatives, Memorial Addresses on Joseph A. Goulden, 1917, p. 97.
- ↑ "Gettysburg Eyewitness – Lost and Found Sound: The Boy Who Heard Lincoln". NPR. Retrieved September 7, 2009.
- ↑ "21 Minute audio recording of William R. Rathvon's audio recollections of Lincoln's Gettysburg Address recorded in 1938". NPR. Retrieved September 7, 2009. and "6 min. version. SMIL file format.". NPR. Retrieved September 7, 2009.
- ↑ "Lost and Found Sound: An American Record Transcript", National Endowment for the Humanities.
- ↑ "The Only Known Photograph of President Lincoln at the dedication of the Civil War cemetery at Gettysburg, Pennsylvania, November 19, 1863". Library of Congress. Retrieved September 15, 2010.
- ↑ "Bachrach in the news". Bachrach photography. Retrieved December 3, 2007.
- ↑ Walker, Cliff (ed.) (September 2002). "Lincoln's Gettysburg 'Under God': Another case of 'retrofitting'? (reply)". Positive Atheism. Retrieved December 3, 2007.
- ↑ Randi, James (October 10, 2003). "Lincoln Embellished". James Randi Educational Foundation. Retrieved December 3, 2007.: "The Gettysburg address ... is often given as the source of the addition to the Pledge of Allegiance that we often hear, that phrase, 'under God.' Wrong."
- ↑ Barton, pp. 138–139.
- ↑ Prochnow, p. 14.
- ↑ Prochnow, p. 13.
- 1 2 Prochnow, p. 15.
- ↑ Sandburg, Carl. "Lincoln Speaks at Gettysburg". In: Abraham Lincoln: The War Years (1939) New York: Harcourt, Brace & Company. II, 452–457; cited by Prochnow, p. 14.
- ↑ Barton, p. 81.
- ↑ Geoff Nunberg (June 20, 2004). "'(Next) Under God,' Phrasal Idiom". Language Log. Retrieved November 24, 2013.
- ↑ Einhorn, Lois (1992). Abraham Lincoln, the orator: penetrating the Lincoln legend. Greenwood Press. p. 92. ISBN 0-313-26168-7. Retrieved April 20, 2012.
- ↑ Historical Marker Database. "Gettysburg Address Marker". Retrieved June 11, 2012.
- ↑ Historical Marker Database. "Lincoln Speech Memorial Marker". Retrieved June 11, 2012.
- ↑ Lincoln Financial Foundation Collection. "Lincoln at Gettysburg; Told by Eye Witness" (PDF). Retrieved June 13, 2012.
- ↑ Lincoln National Life Insurance Company (November 25, 1969). "Dispute Over Exact Location Where Lincoln's Speech Was Made of Great Interest To Many Gettysburg Visitors". Gettysburg Times. pp. 7–9.
- ↑ Pergus Project. "Gettysburg Address". Retrieved June 11, 2012.
- ↑ Tilberg, Frederick. "The Location of the Platform From Which Lincoln Delivered the Gettysburg Address". Pennsylvania History, Vol XL, No. 2. The Pennsylvania Historical Association. pp. 179–191. Retrieved June 13, 2012.
- ↑ Historical Marker Database. "Kentucky Memorial Marker". Retrieved June 11, 2012.
- ↑ Tilberg, Frederick. "The Location of the Platform From Which Lincoln Delivered the Gettysburg Address". Pennsylvania History, Vol XL, No. 2. The Pennsylvania Historical Association. p. 187. Retrieved June 13, 2012.
- ↑ Historical Marker Database. "The Gettysburg Address Marker". Retrieved June 11, 2012.
- ↑ "Soldiers' National Monument". (structure ID MN288, LCS ID 009949) List of Classified Structures: GETT p. 21. National Park Service. 2004 [1865–69]. Retrieved June 22, 2011.
- ↑ National Park Service. "FCIC: Gettysburg National Military Park". Retrieved June 12, 2012.
- ↑ Stone Sentinels. "Soldiers' National Monument". Retrieved June 19, 2012.
- ↑ Waymarking. "Soldiers' National Monument". Retrieved June 19, 2012.
- ↑ Flickr/Jericho_54. "Gettysburg: Soldiers' National Monument". Retrieved June 19, 2012.
- ↑ Historical Marker Database. "The Gettysburg Address". Retrieved June 11, 2012.
- ↑ Waymarking.com. "The Gettysburg Address — Gettysburg, PA — Abraham Lincoln". Retrieved June 15, 2012.
- ↑ Wills, Garry (1992). Lincoln at Gettysburg: The Words That Remade America. New York: Simon and Schuster. pp. 209–210. ISBN 978-0-671-86742-3.
- ↑ The Washington Times. "Disproving Many Historical 'Facts'". Retrieved June 17, 2013.
- ↑ Frassanito, William A. (1995). Early Photography at Gettysburg. Gettysburg, PA: Thomas Publications. pp. 160–167. ISBN 0-939631-86-5.
- ↑ University of North Carolina at Asheville. "Finding the Real Lincoln". Retrieved August 12, 2014.
- ↑ National Park Service. "National Cemetery Walking Tour" (PDF). Retrieved June 12, 2012.
- ↑ Frassanito, William A. (1995). Early Photography at Gettysburg. Gettysburg, PA: Thomas Publications. p. 167. ISBN 0-939631-86-5.
- ↑ Pfanz, Harry W (1993). Gettysburg: Culp's Hill and Cemetery Hill. Chapel Hill, NC: The University of North Carolina Press. p. 375. ISBN 0-8078-2118-7.
- ↑ Gettysburg Discussion Group. "Afterwards and Afterthoughts". Retrieved June 19, 2012.
- ↑ "Outline of U.S. History". United States Department of State. p. 73. Retrieved January 3, 2009.
- ↑ Dry, M. (1996). "Review of National Standards for Civics and Government". PS: Political Science and Politics. 29 (1): 49–53. doi:10.2307/420193.
- ↑ Garrow, David J. (August 2003). "Martin Luther King Jr: the March, the Man, the Dream.". American History. Retrieved November 9, 2009.
[F]our days before the March [King] told Al Duckett, a black journalist ... that his August 28 oration needed to be "sort of a Gettysburg Address".
- ↑ "Constitution du 4 octobre 1958" (PDF). Retrieved October 18, 2009.
- ↑ Sharman, Lyon (1968). Sun Yat-sen: His life and its meaning, a critical biography. Stanford University Press. p. 271.
- ↑ "USS Abraham Lincoln". United States Navy. Carrier Strike Group NINE. Retrieved October 14, 2011.
Aircraft carrier Abraham Lincoln (CVN-72) adopted Lincoln's phrase "Shall not perish" as her motto.
- ↑ "Abraham Lincoln". Dictionary of American Naval Fighting Ships. Navy Department, Naval History & Heritage Command. Retrieved October 14, 2011.
- ↑ "Message from the President on the Occasion of Field Mass at Gettysburg, June 29, 1963, delivered by John S. Gleason, Jr." Box 10, President's Outgoing Executive Correspondence, White House Central Chronological Files, Papers of John F. Kennedy, John F. Kennedy Presidential Library.
- ↑
- Gettysburg Replies: The World Responds to Abraham Lincoln's Gettysburg Address. Lyons Press. 2015. ISBN 1493009125.
- ↑ Neil deGrasse Tyson's Gettysburg Reply – "The Seedbed"
Bibliography
- Barton, William E. (1950). Lincoln at Gettysburg: What He Intended to Say; What He Said; What he was Reported to have Said; What he Wished he had Said. New York: Peter Smith.
- Boritt, Gabor (2006). The Gettysburg Gospel: The Lincoln Speech That Nobody Knows Simon & Schuster. 432 pp. ISBN 0-7432-8820-3.
- Busey, John W., and Martin, David G., Regimental Strengths and Losses at Gettysburg, 4th Ed., Longstreet House, 2005, ISBN 0-944413-67-6.
- Frassanito, William A. (1995). Early Photography at Gettysburg. Gettysburg, PA: Thomas Publications. ISBN 978-1-57747-032-8.
- Gramm, Kent (2001). November: Lincoln's Elegy at Gettysburg. Bloomington: Indiana University Press. ISBN 0-253-34032-2.
- Herndon, William H. and Welk, Jesse W. (1892). Abraham Lincoln: The True Story of A Great Life (Vol II). New York: D. Appleton and Company.
- Kunhardt, Philip B., Jr. (1983). A New Birth of Freedom: Lincoln at Gettysburg. Little Brown & Co. 263 pp. ISBN 0-316-50600-1.
- Lafantasie, Glenn. "Lincoln and the Gettysburg Awakening". Journal of the Abraham Lincoln Association 1995 16(1): 73–89. ISSN 0898-4212.
- McPherson, James M. (1988). Battle Cry of Freedom: The Civil War Era (Oxford History of the United States). Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-503863-0.
- McPherson, James M. (1996). Drawn with the Sword: Reflections on the American Civil War. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-509679-7.
- Murphy, Jim (1992). The Long Road to Gettysburg. New York: Clarion Books. 128 pp. ISBN 0-395-55965-0.
- Prochnow, Victor Herbert. ed. (1944). Great Stories from Great Lives. Freeport: Books for Libraries Press, 1944. ISBN 0-8369-2018-X.
- Rawley, James A. (1966). Turning Points of the Civil War. University of Nebraska Press. ISBN 0-8032-8935-9.
- Reid, Ronald F. "Newspaper Responses to the Gettysburg Addresses". Quarterly Journal of Speech 1967 53(1): 50–60. ISSN 0033-5630.
- Sandburg, Carl (1939). "Lincoln Speaks at Gettysburg". In: Abraham Lincoln: The War Years New York: Harcourt, Brace & Company. II, 452–457. ASIN: B000BPD8GC.
- Sauers, Richard A. (2000). "Battle of Gettysburg". In Encyclopedia of the American Civil War: A Political, Social, and Military History. Heidler, David S., and Heidler, Jeanne T., eds. W. W. Norton & Company. ISBN 0-393-04758-X.
- Selzer, Linda. "Historicizing Lincoln: Garry Wills and the Canonization of the 'Gettysburg Address". Rhetoric Review Vol. 16, No. 1 (Autumn 1997), pp. 120–137.
- Simon, et al., eds. (1999). The Lincoln Forum: Abraham Lincoln, Gettysburg, and the Civil War. Mason City: Savas Publishing Company. ISBN 1-882810-37-6.
- White, Ronald C., Jr. (2005). The Eloquent President: A Portrait of Lincoln Through His Words. New York: Random House. ISBN 1-4000-6119-9.
- Wieck, Carl F. (2002). Lincoln's Quest for Equality: The Road to Gettysburg. Northern Illinois University Press. 224 pp. ISBN 0-87580-299-0.
- Wills, Garry (1992). Lincoln at Gettysburg: The Words That Remade America. New York: Simon and Schuster. 319 pp. ISBN 0-671-76956-1.
- Wilson, Douglas L. (2006). Lincoln's Sword: The Presidency and the Power of Words. Knopf. 352 pp. ISBN 1-4000-4039-6.
Primary sources
- Abraham Lincoln Presidential Library Foundation, ed. Gettysburg Replies: The World Responds to Abraham Lincoln's Gettysburg Address (2015) ISBN 1493009125
External links
| Wikisource has original text related to this article: |
| Wikisource has original text related to this article: |
- Library of Congress, Gettysburg Address exhibit
- Gettysburg National Military Park (GNMP) Gettysburg Historical Handbook
- Online Lincoln Coloring Book for Teachers and Students
- Cornell University Library exhibit on Contemporary newspaper reactions.
- Abraham Lincoln: A Resource Guide from the Library of Congress
- Gettysburg Address read by Sam Waterston, Matthew Broderick, Ken Burns, David McCullough, Stephen Lang, Paul W. Bucha, etc. Music by John Williams.
- Gettysburg Address audio performances by Jeff Daniels, Jim Getty, Johnny Cash, Colin Powell, Sam Waterston, and W. F. Hooley from AmericanRhetoric.com
- The Gettysburg Address An online exhibition from the National Museum of American History, Smithsonian Institution
-
 Gettysburg Address public domain audiobook at LibriVox
Gettysburg Address public domain audiobook at LibriVox
