Global Carbon Project
The Global Carbon Project (GCP) was established in 2001. The organisation seeks to quantify global carbon emissions and their causes.[1]
The main object of the group has been to fully understand the carbon cycle. The project has brought together emissions experts and economists to tackle the problem of rising concentrations of greenhouse gases.
The Global Carbon Project works collaboratively with the International Geosphere-Biosphere Programme, the World Climate Programme, the International Human Dimensions Programme on Global Environmental Change and Diversitas, under the Earth System Science Partnership.
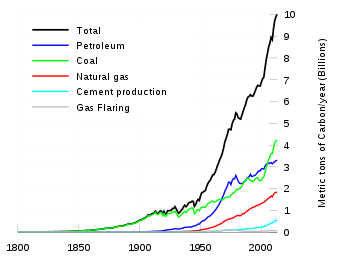
In late 2006 researchers from the project claimed that carbon dioxide emissions had dramatically increased to a rate of 3.2% annually from 2000. At the time, the chair of the group Dr Mike Raupach stated that "This is a very worrying sign. It indicates that recent efforts to reduce emissions have had virtually no impact on emissions growth and that effective caps are urgently needed,".[2]
A 2010 study conducted by the Project and Nature Geoscience revealed that the world's oceans absorb 2.3 billion metric tonnes of carbon dioxide.[3]
On December 5, 2011 analysis released from the project claimed carbon dioxide from fossil-fuel burning jumped by the largest amount on record in 2010 to 5.9 percent from a growth rate in the 1990s closer to 1 percent annually. The combustion of coal represented more than half of the growth in emissions, the report found.[4]
They predict greenhouse gas emissions to occur according to the IPCC's worst-case scenario, as CO2 concentration in the atmosphere reaches 500ppm in the 21st century.
Global Carbon Budget
Established by the GCP in 2005 the Global Carbon Budget is an annual publication of carbon cycle sources and sinks on a global level. In 2013 the annual publication of the Global Carbon Budget became a living data publication at the Earth System Science Data journal. Each year data is revised and updated along with any changes in analysis, results and the most up to date interpretation of the behaviour of the global carbon cycle.
The original measurements and data used to complete the global carbon budget are generated by multiple organizations and research groups around the world.
The effort presented by the GCP is mainly one of synthesis, where results from individual groups are collated, analysed and evaluated for consistency. The GCP facilitate access to original data with the understanding that the primary datasets will be referenced in future work (See Table). In depth descriptions of each component are provided by the original publications associated with those datasets.
| Component | Primary Reference |
|---|---|
| Territorial fossil-fuel and cement emissions globally, by fuel type, and by country | Boden et al. (2013; CDIAC: cdiac.ornl.gov/trends/emis/meth_reg.html)[5] |
| Consumption-based fossil-fuel and cement emissions by country | Peters et al. (2011) [6] updated as described in Le Quéré et al. (2013) [7] |
| Land-use change emissions | Houghton and Hackler (in review) |
| Atmospheric CO2 growth rate | Dlugokencky and Tans (2013; NOAA/ESRL: www.esrl.noaa.gov/gmd/ccgg/trends/)[8] |
| Ocean and land CO2 sinks | Le Quéré et al. (2013) [7] see references in paper for individual models. |
Global Carbon Atlas
Established by the GCP in 2013 the Global Carbon Atlas is a tool for the visualisation of data related to the global carbon cycle.
The Global Carbon Atlas is a platform to explore and visualize the most up-to-date data on carbon fluxes resulting from human activities and natural processes. Human impacts on the carbon cycle are the most important cause of climate change.
This web-based application allows the dissemination of the most up to date information on the global carbon cycle to a wider audience from the school children and lay people to policy makers and scientists. It consists of three components 1) Outreach, 2) Emissions and 3) Research. The outreach component is aimed at the general public and those working in education. The emissions component is a visualisation tool for parts of the global carbon cycle that are related to emissions and is aimed primarily at policy makers. The research component is aimed primarily at researchers and acts as a data repository and visualisation tool for scientific data that is used to investigate the global carbon budget.
All components of the Global Carbon Atlas are updated on an annual basis, based on the data published in the Global Carbon Budget, with the most up to date data and interpretation of carbon cycle processes.
See also
- AIMES (Analysis, Integration and Modelling of the Earth System)
- List of countries by carbon dioxide emissions
References
- ↑ About GCP. Retrieved on 5 February 2011.
- ↑ Global growth in carbon emissions is 'out of control'. Steve Connor. Published on 11 November 2006. Retrieved on 23 May 2007.
- ↑ Dahr Jamail (22 November 2011). "World's oceans in peril". Al Jazeera. Retrieved 5 December 2011.
- ↑ Carbon Emissions Show Biggest Jump Ever Recorded Justin Gillis. Published on December 4, 2011. Retrieved on December 5th 2011.
- ↑ Fossil-Fuel CO2 Emissions. Boden et al 2013. Published in July 2013. Retrieved on 18 November 2013.
- ↑ Growth in emission transfers via international trade from. Peters et al. Published on 11 May 2011. Retrieved on 18 November 2013.
- 1 2 Global Carbon Budget 2013. Le Quéré et al. Published on 19 November 2013. Retrieved on 19 November 2013.
- ↑ Annual Mean Global Carbon Dioxide Growth Rates. Dlugokencky and Tans. Published in December 2012. Retrieved on 18 November 2013.
External links
- Global Carbon Project's website
- Global Carbon Atlas' website
- Global Carbon Budget's website
- Earth System Science Partnership's website
