Guimarães
| Guimarães | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Municipality | |||
|
Clockwise from top left: Guimarães Castle, a chimney at the Duke of Braganza's Palace, statue of Dom Afonso Henriques at the Ducal Palace, Oliveira Plaza, panoramic view of Guimarães historical heritage area from Mount Penha, Santa Maria Street, Santiago Plaza | |||
| |||
 | |||
| Coordinates: 41°27′N 8°18′W / 41.450°N 8.300°WCoordinates: 41°27′N 8°18′W / 41.450°N 8.300°W | |||
| Country |
| ||
| Region | Norte | ||
| Subregion | Ave | ||
| Intermunic. comm. | Ave | ||
| District | Braga | ||
| Parishes | 48 | ||
| Government | |||
| • President | Domingos Bragança (PS) | ||
| Area | |||
| • Total | 241.3 km2 (93.2 sq mi) | ||
| Population (2011) | |||
| • Total | 158,124 | ||
| • Density | 660/km2 (1,700/sq mi) | ||
| Time zone | WET/WEST (UTC+0/+1) | ||
| Website |
www | ||
| Historic Centre of Guimarães | |
|---|---|
| Name as inscribed on the World Heritage List | |
 Aerial view of the Palace of the Dukes of Braganza (From IPPAR) | |
| Type | Cultural |
| Criteria | ii, iii, iv |
| Reference | 1031 |
| UNESCO region | Europe and North America |
| Inscription history | |
| Inscription | 2001 (25th Session) |


Guimarães (Portuguese pronunciation: [ɡimɐˈɾɐ̃jʃ]) is a city and municipality located in northern Portugal, in the district of Braga. Its historic town center is listed as UNESCO World Heritage Site since 2001, in recognition for being an exceptionally well-preserved and authentic example of the evolution of a medieval settlement into a modern town in Europe.
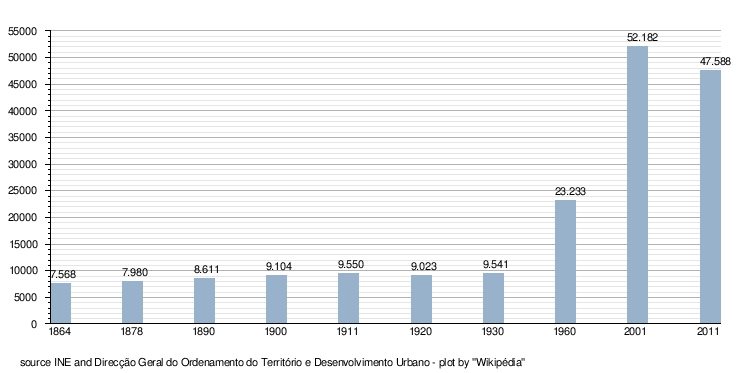
Guimarães is also a part of the Ave Subregion (one of the most industrialised subregions in the country), as well as the historical Minho Province. The city has a population of 52,181 inhabitants.[1] The population of the municipality in 2011 was 158,124,[2] in an area of 240.95 square kilometres (93.03 sq mi).[3] The current Mayor is Domingos Bragança, of the Socialist Party. The municipality is bordered to the north by the municipality of Póvoa de Lanhoso, to the east by Fafe, to the south by Felgueiras, Vizela and Santo Tirso, to the west by Vila Nova de Famalicão and the northwest by Braga.
The city was settled in the 9th century, at which time it was called Vimaranes. This denomination might have had its origin in the warrior Vímara Peres, who chose this area as the main government seat for the County of Portugal which he conquered for the Kingdom of Galicia.
Guimarães has a significant historical importance due to the role it played in the foundation of Portugal. The city is often referred to as the "birthplace of the Portuguese nationality" or "the cradle city" (Cidade Berço in Portuguese) because it is widely believed that Portugal's first King, Afonso Henriques, was born there, and also due to the fact that the Battle of São Mamede - which is considered the seminal event for the foundation of the Kingdom of Portugal - was fought in the vicinity of the city.[4]
For some decades, Guimarães was the capital of the County of Portugal, however, shortly after the Battle of São Mamede (1128), and due to the needs of the Reconquista, Coimbra became the kingdom's capital.[5]
The inhabitants of Guimarães are often called "Vimaranenses" and "Conquistadores" (the Conquerors) in relation with the historical heritage of the conquest initiated in Guimarães.
Guimarães, along with Maribor, Slovenia, was the European Capital of Culture in 2012.
History

The History of Guimarães is associated with the foundation and identity of the Portuguese nationality. Guimarães, as well as other settlements, precedes the foundation of Portugal and because of its role in the foundation of the country it is known as the "cradle of the Portuguese nationality". In 1128, major political and military events that would lead to the independence and the birth of a new nation took place in Guimarães. For this reason, in one of the old towers of the city's old wall it is written "Aqui nasceu Portugal" (Portugal was born here).
Pre- and protohistory
According to archeological findings in Citânia (Castro) of Briteiros and Sabroso and Penha's archeologic site, the area in which Guimarães is located has had permanent settlements since the late Chalcolithic period.
There is also evidence of Roman occupation and a stone dedicated to the Roman emperor Trajan found in Caldas das Taipas suggests that this was already a spa town in Roman times.[6]
From the foundation of Guimarães to the foundation of Portugal

Following the Reconquista policy promoted by the Kingdom of Galicia in the 9th century, the medieval foundations of the actual city have roots in the 10th century. At this point, the Countess Mumadona Dias, erected a monastery in her property of Vimaranes, which originated the fixation of people in the area known as "vila baixa" (downtown). At the same time, she ordered the construction of a castle on the hill area which became known as "vila alta" (uptown), to defend the settlement. To connect these to other areas, the Rua de Santa Maria was built.
The monastery became the "Real Colegiada" (Royal Collegiate church) and throughout time acquired importance due to the privileges and donations given to it by nobles and kings and it became a famous pilgrimage site.
Henry, Count of Portugal approved the first national foral possibly in 1096 (but not confirmed). The foral proves the growing importance of the village of Guimarães at that time, which was chosen as the capital of the County of Portugal.
On 24 June 1128, the "Batalha de São Mamede" (Battle of São Mamede) took place in Guimarães.
Middle Ages
During the reign of king Denis, as the village was expanding, it was partially surrounded by a defensive wall. Meanwhile, mendicant orders settled in Guimarães and helped to mold the shape of the emerging city. Later, during the reign of John I, the wall was torn down and the two parts of the city (uptown and downtown) were finally united and the city began to expand outside its old walls.
Modern and contemporary
Until the 19th century the structure of the city did not suffer many transformations besides the construction of a few more churches, convents and palaces. It was by the ending of the 19th century that new urbanistic ideas of hygiene and symmetry that the village, that was promoted to city by the Queen Maria II on 23 June 1853 had its greatest changes.
The complete demolition of the city walls was authorized and the creation of many streets and avenues could start at that point. The controlled process of urbanization permitted the conservation of the city's magnificent historical center.
Geography
Geology
Granite rock formations occupy the majority of the municipality but schist rocks can also be found in certain zones in the northwest of the municipality. On the southeast, clay can be found in stream bed of the Ave, Vizela and Selho rivers.
Orography and hydrography

The municipality is delimited at north by the "Senhora do Monte" (Senhora hill), at northwest by the hills of Falperra, Sameiro, Outeiro and Penedice. To the south by the Penha hill which with height of 613 meters, it is the highest point of the municipality.
Guimarães is part of the drainage basin of Ave river which divides the municipality in half. The Ave river has as tributaries the Vizela river, Torto river, Febras river and inside the city, the Selho river, the Couros river and the Santa Lúzia stream.
Climate
Guimarães is located in a valley and surrounded by hills and because there is some distance to the sea, the Winter is normally cold and rainy and the Summer is hot and lightly humid. The average annual temperature is 14 °C.
Fauna

There is not much diversity, specially in the urban areas, but the municipality has some species of cynegetic interest such as: the red fox, the wild boar, the turtle dove, the thrush, the pigeon and the red-legged partridge. In the green areas of the city, the most common species are rodents, especially squirrels.
Parishes
Administratively, the municipality is divided into 48 civil parishes (freguesias):[7]
- Abação e Gémeos
- Airão Santa Maria, Airão São João e Vermil
- Aldão
- Arosa e Castelões
- Atães e Rendufe
- Azurém
- Balazar
- Barco
- Briteiros Salvador e Briteiros Santa Leocádia
- Briteiros Santo Estêvão e Donim
- Brito
- Caldas das Taipas (Caldelas)
- Candoso (São Martinho)
- Candoso São Tiago e Mascotelos
- Conde e Gandarela
- Costa
- Creixomil
- Fermentões
- Gonça
- Gondar
- Guardizela
- Infantas
- Leitões, Oleiros e Figueiredo
- Longos
- Lordelo
- Mesão Frio
- Moreira de Cónegos
- Nespereira
- Oliveira, São Paio e São Sebastião
- Pencelo
- Pinheiro
- Polvoreira
- Ponte
- Prazins (Santa Eufémia)
- Prazins Santo Tirso e Corvite
- Ronfe
- Sande São Lourenço e Balazar
- Sande (São Martinho)
- Sande Vila Nova e Sande São Clemente
- São Torcato
- Selho (São Cristóvão)
- Selho (São Jorge)
- Selho São Lourenço e Gominhães
- Serzedelo
- Serzedo e Calvos
- Silvares
- Souto Santa Maria, Souto São Salvador e Gondomar
- Tabuadelo e São Faustino
- Urgezes
Demographics
In 2001, the population of the municipality was 159 576. In 2010, it is estimated that the population will reach 188 178 inhabitants. The population is constituted by 78 436 males and 81 140 females. Guimarães is the 13th biggest city in the country in terms of population.
- Evolution of the population of the municipality of Guimarães (1801–2011)

- Evolution of the population in the city center (1864–2011)
Culture

Guimarães is an average size city but with a booming cultural life. Besides its museums, monuments, cultural associations, art galeries and popular festivities, it has since September 2005, an important cultural space, the Vila Flor Cultural Center. This cultural center has two auditoria, exhibition center and a concert-cafe. Guimarães was the European Capital of Culture in 2012, together with Maribor.
Guimarães was elected by the New York Times one of the 41 places to go in 2011 and NYT called it one of the Iberian peninsula's emerging cultural spots.[8]
Gastronomy

The fact that since its beginning, Guimarães had a feminine monastery made much influence over its regional gastronomy, specially its confectionery. "Tortas de Guimarães" (Guimarães' pies) and "Toucinho do céu" (normally translated as bacon from heaven) are a good example. Besides the customary Minho gastronomy, the so-called "meat" cake is made here, which is a kind of bread in a pizza shape served with pig, sardines or other toppings.
Traditions and festivities
- "Festas Gualterianas" (Gualterianas fest), in honor of Saint Gualter, take place since 1906 in the first weekend of August. The "Cortejo do Linho" (Linen parade) and the "Batalha das Flores" (Battle of the Flowers) are part of the festivities which are ended by the "Marcha Gualteriana" (Gualteriana march).
- "Nicolinas" are the festivities of the students of Guimarães, celebrated in honor of Saint Nicholas. The festivities start on 29 November and finish 7 December. They are composed of different celebrations; the "Pinheiro" is most widely attended. After a restaurant dinner, the participants parade the streets of Guimarães playing the "Toques Nicolinos" tune on drums. Latelly, it has been suggested that the "Nicolinas" should be a contender to be UNESCO intangible cultural heritage.
- The Santa Luzia festivities in honor of honor Saint Lucy take place annually on 13 December, near to the chapel of Santa Luzia. The selling of traditional cakes made of rye and sugar, which are called "Sardão" and "Passarinha" (these names have sexual connotations in Portuguese). According to the tradition, a boy should offer a "Sardão", which has a phallic form, to the girl and if the girl was interested in dating the boy, she should reply with a "Passarinha".
- The "Big Romaria of São Torcato" is one of the biggest romarias in Minho, takes place annually in July in the village of São Torcato.
Museums, cultural spaces and art galleries

The city of Guimarães has several cultural spaces of reference at a regional and national level. Among the several museums of the city, the Alberto Sampaio museum is the one that stands out. Founded in 1928, it opened its doors to the public in 1931; it is located in the old site of the Canon the Collegiate of Our Lady of Oliveira (Cabido da Colegiada de Nossa Senhora da Oliveira in Portuguese). It contains a rich collection of pieces from the 14th, 15th and 16th century, including one rare vest that was used by the king John I.
The Martins Sarmento Society (Sociedade Martins Sarmento in Portuguese) is one of the country oldest institutions dedicated to the study and preservation of archaeological artifacts. The society owns two museums: the Archaeological Museum of the Martins Sarmento Society, which is known by its prehistory and protohistory collections and also its numismatics and epigraphy collections; and the Castro Culture Museum which is dedicated to the Castro culture.
There is also: the Primitive Modern Arts Museum, located in the Domus Municipalis (the old city hall), which contains a collection of naïve art; the Museum of the Village of São Torcato, which is dedicated to the region and its relationship with the monastery and Saint Torcato (São Torcato in Portuguese); the Agriculture Museum of Fermentões, which exhibits collections of the traditional agricultural practices of the region; and the Museum of São Sebastião, inaugurated on 24 March 1984, which contains mainly sacred art.
Other cultural venues include:
- Vila Flor Cultural Center (Centro Cultural Vila Flor in Portuguese) is the main cultural venue in Guimarães. It was built in 2005, in a recovery of the old Vila Flor Palace and its surrounding area. It has two auditoriums, a concert-cafe and an exhibition gallery. The surrounding gardens of the old palace were also redone and in 2006, received an honorable mention in the Public Exterior Spaces category in the National Landscape Architecture Award.
- São Mamede - Guimarães Arts and Shows Center.
- Raul Brandão Municipal Library has its headquarters in the city and also has branches in Pevidém, Caldas das Taipas and Ronfe. It offers its mobile library services to 42 parishes and services the city schools and prison.
- The Art Laboratory (Laboratorio das Artes in Portuguese) was founded in 2004 by ESAP students. It is a cultural space for exhibitions, performances, music and art workshops.
- Alfredo Pimenta National Archive, founded in 1931, contains the archives for municipality of Guimarães and also the Braga district.
Sports
Guimarães has a major sports club, Vitória Sport Clube, whose football (soccer) team has been the city's representative in the Primeira Liga for many years. Vitória SC also has basketball and volleyball squads competing in the top divisions of their sports.
Society
In 2008, the city ranked second in the index of most livable city in Portugal. It is also the second least polluted city in the country.
In 2004, 89% of the population had running water; it was forecast that the number would raise to 95% by 2006. In 2001, 63.5% of the population had basic sanitation; it was forecast that the number would raise to 80% by 2008. In 2001, 100% of the population had access to waste management services.
However, several people complain that the city, together with other cities of the Braga district has had an unaesthetic and unorganized growth.
Social media
Newspapers
Guimarães ranks fourth in the country for available newspapers. The oldest was the "Azemel Vimaranense", founded in 1822; it possibly had its publication halted by the Vilafrancada incidents. From 1856, other newspapers start to appear, amongst them "A Tesoura de Guimarães". Actually the citys' newspapers are:
- O Comércio de Guimarães
- O Cónego
- O Conquistador
- Desportivo de Guimarães
- Entrevillas
- O Expresso do Ave
- Jornal do Adepto
- Lordelo Jornal
- O Pilar
- O Povo de Guimarães
- Notícias de Guimarães
- Reflexo – O Espelho das Taipas]]
- Sport Jornal dos Desportos
Radios
There are two stations headquartered in the town: Radio Fundação (95.8 FM) and Radio Santiago (98.0 FM).
Television
The Guimarães TV transmission is made online since 24 July 2007; it is the result of a collaboration between the city's assembly and the Guimarães Cybercenter. Its contents are feature in the Região Norte TV channel which is available through cable.
The "canalguimarães" is another online channel that started operating in March 2010. It is the fruit of the effort put in by an arts association, the "Associação de Socorros Mútuos Artística Vimaranense", one of the oldest associations of the city.
Economy
Guimarães is one of the most industrial municipalities in Portugal. Its primary industries are textiles, shoe industry and metalomechanics.
Transport
Guimarães is linked to Porto by the Guimarães line. This railway line was originally built with narrow gauge track, then modernised and rebuilt to the broad Iberian gauge in the first decade of the 21st century. The train service is operated by Comboios de Portugal (CP). Locally, Guimarães is served by TUG (Transportes Urbanos de Guimarães) which operates 21 bus routes serving the city.
International relations
Guimarães is twinned with:
|
|
Notable people
|
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Guimarães. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Guimarães. |
- Municipality official website
- Tourism in Guimarães
- Photos from Guimarães
- Guimarães 2012
- Guimarães 2012 - Cultural Programme on e-book format
- Guimarães: 2012 European Capital of Culture - Portugal, Portuguese American Journal
References
- ↑ http://www.dgotdu.pt/PresentationLayer/ResourcesUser/DGOTDU/EstudosNaoPublicados/Guimaraes/GUIMARAES.pdf
- ↑ Instituto Nacional de Estatística
- ↑ Direção-Geral do Território
- ↑ História de Portugal - Battle of Sao Mamede
- ↑ Condado Portucalense - História de Portugal (in Portuguese)
- ↑ Portugal Romano - Ara de Trajano (in Portuguese)
- ↑ Diário da República. "Law nr. 11-A/2013, pages 552 56-58" (pdf) (in Portuguese). Retrieved 23 July 2014.
- ↑ Wilder, Charly "The New York Times", 9 January 2011
- ↑ "Lisboa - Geminações de Cidades e Vilas" [Lisbon - Twinning of Cities and Towns]. Associação Nacional de Municípios Portugueses [National Association of Portuguese Municipalities] (in Portuguese). Retrieved 2013-08-23.
- ↑ "Acordos de Geminação, de Cooperação e/ou Amizade da Cidade de Lisboa" [Lisbon - Twinning Agreements, Cooperation and Friendship]. Camara Municipal de Lisboa (in Portuguese). Retrieved 2013-08-23.



