Rapadilino syndrome
| Rapadilino syndrome | |
|---|---|
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | medical genetics |
| ICD-10 | Q87.1 |
| OMIM | 266280 |
| DiseasesDB | 34465 |
Rapadilino syndrome is an autosomal recessive[1] congenital disorder characterized by radial and patellar aplasia, short stature, arched or cleft palate, limb malformation, and dislocated joints.[1] It is more prevalent in Finland than elsewhere in the world.
It has been associated with RECQL4.[2] This is also associated with Rothmund-Thomson syndrome[3] and Baller-Gerold syndrome.[4]
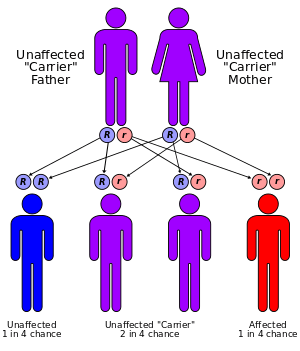
Rapadilino syndrome has an autosomal recessive pattern of inheritance.
External links
References
- 1 2 Kaariainen H, Ryoppy S, Norio R (1989). "Rapadlino syndrome with radial and patellar aplasia/hypoplasia as main manifestations". Am J Med Genet. 33 (3): 346–351. doi:10.1002/ajmg.1320330312. PMID 2801769.
- ↑ Siitonen HA, Kopra O, Kääriäinen H, et al. (November 2003). "Molecular defect of RAPADILINO syndrome expands the phenotype spectrum of RECQL diseases". Hum. Mol. Genet. 12 (21): 2837–44. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddg306. PMID 12952869.
- ↑ Yin J, Kwon YT, Varshavsky A, Wang W (October 2004). "RECQL4, mutated in the Rothmund-Thomson and RAPADILINO syndromes, interacts with ubiquitin ligases UBR1 and UBR2 of the N-end rule pathway". Hum. Mol. Genet. 13 (20): 2421–30. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddh269. PMID 15317757.
- ↑ Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) 218600
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 5/27/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.
