Zhemchug Canyon
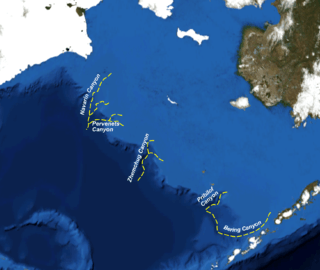
Zhemchug Canyon is an underwater canyon located in the middle of the Bering Sea. This submarine canyon is the deepest and is tied for widest canyon in the ocean.[1] It has a vertical relief of 8,530 feet or 2,600 meters dropping from the shallow shelf of the Bering Sea to the depths of the Aleutian Basin.[1] Zhemchug Canyon is deeper than the Grand Canyon which is 6,093 feet or 1,857 meters deep.[2] It has two main branches, each larger than typical continental margin canyons such as the Monterey Canyon. What makes the Zhemchug Canyon the world's largest is not only its great depth, but its immense cross-sectional and drainage area, (11,350 km2) and volume (5800 km3).[1]
In 2016, Michelle Ridgeway explored the canyon piloting an eight-foot submarine in an expedition sponsored by Greenpeace. She reached a shelf at a depth of 1,757 feet or 536 meters, that is, a third of a mile below the surface.[3]
Ocean wildlife
Zhemchug Canyon is important habitat for many species of ocean wildlife. The endangered short-tailed albatross congregates to feed over the surface waters of the canyon. Marine mammals such as northern fur seals feed in the canyon as do dolphins and many species of whales. Habitat-forming invertebrates such as bubblegum coral, bamboo coral, soft corals, Hexactinellid sponges, and other sponges have been identified during trawl surveys in the canyon. It is where the opilio (snow) crab and bairdi crab can be found.
References
- 1 2 3 Normark, W.R. and Carlson, P.R., 2003, Giant submarine canyons: Is size any clue to their importance in the rock record? Archived January 10, 2009, at the Wayback Machine. in Chan, M.A., and Archer, A.W., eds., Extreme depositional environments: Mega end members in geologic time: Boulder, Colorado, Geological Society of America Special Paper 370, p. 1–15
- ↑ Kiver, E.P.; Harris, D.V. (1999). Geology of US Parklands. Wiley. p. 902.
- ↑ Alaska researcher made tantalizing discoveries in a massive underwater Bering Sea canyon, Alaska Dispatch News, Ned Rozell, November 12, 2016. Retrieved 15 November 2016.
Coordinates: 58°06′04″N 174°54′07″W / 58.101°N 174.902°W
