Albatros C.III
| Albatros C.III | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Role | General purpose |
| Manufacturer | Albatros Flugzeugwerke DAR |
| Introduction | 1916 |
| Primary users | Luftstreitkräfte Polish Air Force Finnish Air Force Bulgarian Air Force Lithuanian Air Force |
|
| |
The Albatros C.III was a German two-seat general-purpose biplane of World War I, built by Albatros Flugzeugwerke. The C.III was a refined version of the successful Albatros C.I and was eventually produced in greater numbers than any other C-type Albatros.
Use
The C.III was used in a wide variety of roles including observation, photo-reconnaissance, light bombing and bomber escort. Eighteen C.IIIs were delivered in August 1916 to Bulgaria. They were destroyed in 1920 in accordance with the Treaty of Neuilly-sur-Seine. According to other sources, 26 Albatros C.III were delivered to Bulgaria, including eight trainers.[1]
Construction
Like the Albatros C.I, the C.III was a popular aircraft with rugged construction and viceless handling. The most prominent difference between the two was the revised vertical stabilizer. The C.III had a lower, rounded tail compared to the large, triangular tail of the C.I, which gave the C.III greater agility. The power plant was either a 110 kW (150 hp) Benz Bz. III or a 120 kW (160 hp) Mercedes D.III inline engine and, like numerous other two-seaters used during the war (such as the British Royal Aircraft Factory R.E.8) the cylinder head and exhaust manifold protruded above the front fuselage, limiting the pilot's forward visibility.
The observer, who occupied the rear cockpit, was armed with a single 7.92 mm (0.312 in) Parabellum MG14 machine gun. Some C.III aircraft were fitted with a gun synchronizer and a single forward-firing 7.92 mm (0.312 in) LMG 08/15 machine gun. The C.III could also carry a bomb load of up to 90 kg (200 lb) in a small internal bomb bay.
Between 1926 and 1927, two Mercedes D.III engined copies were built from saved parts and components of the destroyed aircraft by Bulgarian state aircraft workshops DAR as the DAR 2 for use as trainers.[2][3] According to D. Nedialkov, twelve DAR-2 were built (at least nine are confirmed by a photograph).[4]
Operators

- Bulgarian Air Force (including DAR-2)
Variants
Data from[5]
- C.VI
- about 300 mm (11.8 in) shorter and 20 kg (44 lb), with strengthened engine bearers to take a 180 hp (130 kW) Argus As III six-cylinder inline. Some 4% faster. Limited production.
- W.2
- Seaplane variant with twin floats, modified Mercedes D.II istallation, revised cabane struttage and a much larger fin. Parabellum MG14 machine gun in observer's cockpit. One only, delivered June 1916.
Specifications (C.III)
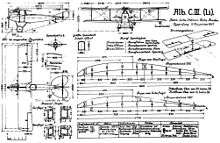
Data from [6]
General characteristics
- Crew: two
- Length: 8.0 m (26 ft 3 in)
- Wingspan: 11.69 m (38 ft 4 in)
- Height: 3.10 m (10 ft 2 in)
- Wing area: 36.91 m² (397 ft²)
- Empty weight: 851 kg (1,876 lb)
- Max. takeoff weight: 1,353 kg (2,983 lb)
- Powerplant: 1 × Benz Bz.III, 112 kW (150 hp) or Mercedes D.III liquid-cooled inline engine, 120 kW (160 hp)
Performance
- Maximum speed: 140 km/h (76 kn, 87 mph)
- Service ceiling: 3,350 m (11,000 ft)
- Endurance: 4 hours
Armament
- Guns: 1 × 7.92 mm (.312 in) Parabellum MG14 machine gun in observer's cockpit and 1 × 7.92 mm MG 08 in the nose
- Bombs: up to 200 lbs of bombs
See also
- Related development
- Aircraft of comparable role, configuration and era
- Related lists
References
- ↑ Nedialkov, Dimitar. "Air Power of the Kingdom of Bulgaria. Part II", Fark OOD, Sofia, 2001. pp.22-23, 28-29. (bilingual: Bulgarian/English)
- ↑ Bernád 2001, pp. 24–25.
- ↑ Y. Milanov: Aviation in Bulgaria in the Wars from 1912 to 1945, Vol.I. Sveti Gueorgui Pobedonosetz, Sofia, 1995 (in Bulgarian)
- ↑ Nedialkov, Dimitar. "Air Power of the Kingdom of Bulgaria. Part III", Fark OOD, Sofia, 2001. pp.4, 20-21, 59. (bilingual: Bulgarian/English)
- ↑ Gray, Peter; Thetford, Owen (1970). German Aircraft of the First World War. London: Putnam. p. 256. ISBN 0-85177-809-7.
- ↑ Sharpe, Michael. Biplanes, Triplanes, and Seaplanes, pg.28. London, England: Friedman/Fairfax Books , 2000. ISBN 1-58663-300-7.
- Bernád, Dénes. "Balkan Birds: Thirty Five Years of Bulgarian Aircraft Production". Air Enthusiast. Stamford, Lincs, UK: Key Publishing (94, July/August 2001): 18–30. ISSN 0143-5450.
External links
![]() Media related to Albatros C.III at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Albatros C.III at Wikimedia Commons