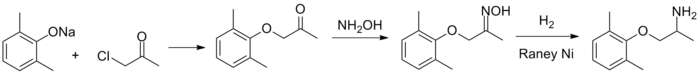Mexiletine
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a607064 |
| Pregnancy category | |
| Routes of administration | Oral, IV |
| ATC code | C01BB02 (WHO) |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 90% |
| Protein binding | 50-60% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic (CYP2D6 and 1A2- mediated) |
| Biological half-life | 10-12 hours |
| Excretion | Renal (10%) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
31828-71-4 |
| PubChem (CID) | 4178 |
| IUPHAR/BPS | 2629 |
| DrugBank |
DB00379 |
| ChemSpider |
4034 |
| UNII |
1U511HHV4Z |
| KEGG |
D08215 |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:6916 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL558 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.046.190 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C11H17NO |
| Molar mass | 179.259 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| Chirality | Racemic mixture |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Mexiletine (INN) (sold under the trade name Mexitil) is a non-selective voltage-gated sodium channel blocker which belongs to the Class IB anti-arrhythmic group of medicines.[1] It is used to treat arrhythmias within the heart, or seriously irregular heartbeats. It slows conduction in the heart and makes the heart tissue less sensitive. Dizziness, heartburn, nausea, nervousness, trembling, unsteadiness are common side effects. It is available in injection and capsule form.
Class IB antiarrhythmics decrease action potential frequency by lengthening the repolarization phase. This is achieved by blocking sodium channels.[2]
This drug is now no longer freely available as a licensed product in either the US or the UK. It can be imported to the UK as an unlicensed, 'named-patient' drug. Its use in arrhythmias is restricted to use in life-threatening conditions only.
Mexiletine may also be of use in patients experiencing refractory pain[3] and is also effective for treating muscle stiffness resulting from myotonic dystrophy (Steinert's disease) or nondystrophic myotonias such as myotonia congenita (Thomsen disease).
Synthesis
References
- ↑ Mexiletine, RxList.com
- ↑ Sweetman S (ed.) (2002). Martindale: The complete drug reference (33rd ed.). London: Pharmaceutical Press. ISBN 0-85369-499-0.
- ↑ H. Koppe, W. Kummer, U.S. Patent 3,954,872 (1976).
- ↑ H. Koppe, W. Kummer, U.S. Patent 3,659,019 (1972).
- ↑ C.H. Boehringer Sohns, Fr 1551055 (1968).
- ↑ H. Koppe, W. Kummer, U.S. Patent 4,031,244 (1977).
Further reading
- Peck T; Hill S, Williams M (eds.) (2004). Pharmacology for Anaesthesia and Intensive Care (2nd ed.). Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-68794-2. Cite uses deprecated parameter
|coauthors=(help)