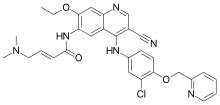
Neratinib
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | none |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
698387-09-6 |
| PubChem (CID) | 9915743 |
| IUPHAR/BPS | 5686 |
| ChemSpider |
8091392 |
| UNII |
JJH94R3PWB |
| KEGG |
D08950 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL180022 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C30H29ClN6O3 |
| Molar mass | 557.04 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
| | |
Neratinib (HKI-272) is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor[1][2] under investigation for the treatment of breast cancer[3] and other solid tumours.
It is in development for the treatment of early- and late-stage HER2-positive breast cancer.[4]
Like lapatinib and afatinib, it is a dual inhibitor of the human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (Her2) and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) kinases.[5]
Clinical trials
Neratanib is being developed by Puma Biotechnology. It will be included in the forthcoming I-SPY2 breast cancer trial.[6]
Mechanism of action
Neratinib inhibits the epidermal growth factor receptor by covalently binding with a cysteine side chain in that protein.[7]
Biological Activity of Neratinib
Neratinib(HKI-272) IC50,respectively, 59, nM, HER2 and epidermal growth factor receptor available and irreversible tyrosine kinase inhibitors. In vivo:Neratinib weakly inhibition of tyrosine kinase KDR and Src, IC50 were 0.8 um and 1.4 um, respectively, being 14- and 24-fold less active compared with HER2. Neratinib for BT474 cells, mainly used to reduce the HER2 receptor autophosphorylation and IC50 were used to reduce the proliferation of A431 cells of 5 nm and 3 nM.Neratinib for BT474 cells and inhibition of cyclin D1 expression of phosphorylated and Rb-Rb- sensitivity of gene product phosphorylation and IC50 for 9 nm, and reduced cell proliferation is reduced, so as to make a cell cycle arrest in G1. In vivo: Neratinib was administered orally at doses of 10, 20,, 40, and 80mg/kg, each day, to inhibit the growth of 3T3/neu transplanted tumors. At the same time, the daily dose of Neratinib was 5 and 60mg/kg, which could significantly inhibit the growth of SK-OV-3 transplanted tumor.[8]
References
- ↑ "Definition of neratinib - National Cancer Institute Drug Dictionary". Retrieved 2008-12-01.
- ↑ Rabindran SK, Discafani CM, Rosfjord EC, et al. (June 2004). "Antitumor activity of HKI-272, an orally active, irreversible inhibitor of the HER-2 tyrosine kinase". Cancer Res. 64 (11): 3958–65. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-03-2868. PMID 15173008.
- ↑ Clinical trial number NCT00398567 for "A Phase 1/2 Study Of HKI-272 In Combination With Herceptin In Subjects With Advanced Breast Cancer" at ClinicalTrials.gov
- ↑ "Puma Acquires Global Rights to Pfizer's Phase III Breast Cancer Drug Neratinib".
- ↑ Minami Y, Shimamura T, Shah K, et al. (July 2007). "The major lung cancer-derived mutants of ERBB2 are oncogenic and are associated with sensitivity to the irreversible EGFR/ERBB2 inhibitor HKI-272". Oncogene. 26 (34): 5023–7. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1210292. PMID 17311002.
- ↑ http://www.reuters.com/article/idUSN1612347120100317 "Breast cancer study aims to speed drugs, cooperation" March 2010
- ↑ http://www.biomedicale.univ-paris5.fr/enseignement/toxico/M2THERV_2013_2014/documents/C15/DANSETTE/EH_CB_RM_M2/CovalentDrug_Baillie_nrd3410.pdf
- ↑ https://www.medchemexpress.com/Neratinib.html
