Sabouraud agar

Bottom view of a Sabouraud agar plate with a colony of Trichophyton rubrum var. rodhaini.
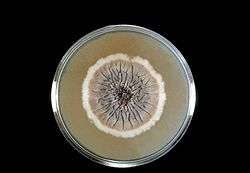
Sporothrix schenckii in Sabouraud agar
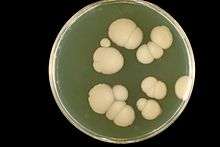
Candida albicans in Sabouraud agar
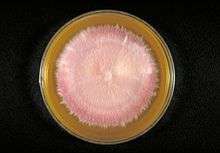
Trichophyton terrestre in Sabouraud agar.
Sabouraud agar is a type of agar containing peptones.[1] It is used to cultivate dermatophytes and other types of fungi, and can also grow filamentous bacteria such as Nocardia.[2][3][4]
It was created by, and is named after, Raymond Sabouraud in 1892. Later adjusted by Chester W. Emmons when the pH level was brought closer to the neutral range and the dextrose concentration lowered to support the growth of other fungi. The 5.6 pH of traditional Sabouraud agar formulation inhibits bacterial growth.
Typical composition
Sabouraud agar typically contains:[5]
References
- ↑ "Omnipresence of Microorganisms in the Environment". Retrieved 2008-10-24.
- ↑ Sandven P; Lassen J (November 1999). "Importance of selective media for recovery of yeasts from clinical specimens". Journal of clinical microbiology. 37 (11): 3731–2. PMC 85742
 . PMID 10523586.
. PMID 10523586. - ↑ Guinea J; Peláez T; Alcalá L; Bouza E (December 2005). "Evaluation of Czapeck agar and Sabouraud dextrose agar for the culture of airborne Aspergillus conidia". Diagnostic microbiology and infectious disease. 53 (4): 333–4. doi:10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2005.07.002. PMID 16263232.
- ↑ About Modified Sabouraud Agar
- ↑ University of Sydney, Recipes.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 11/11/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.
